Figure 2.
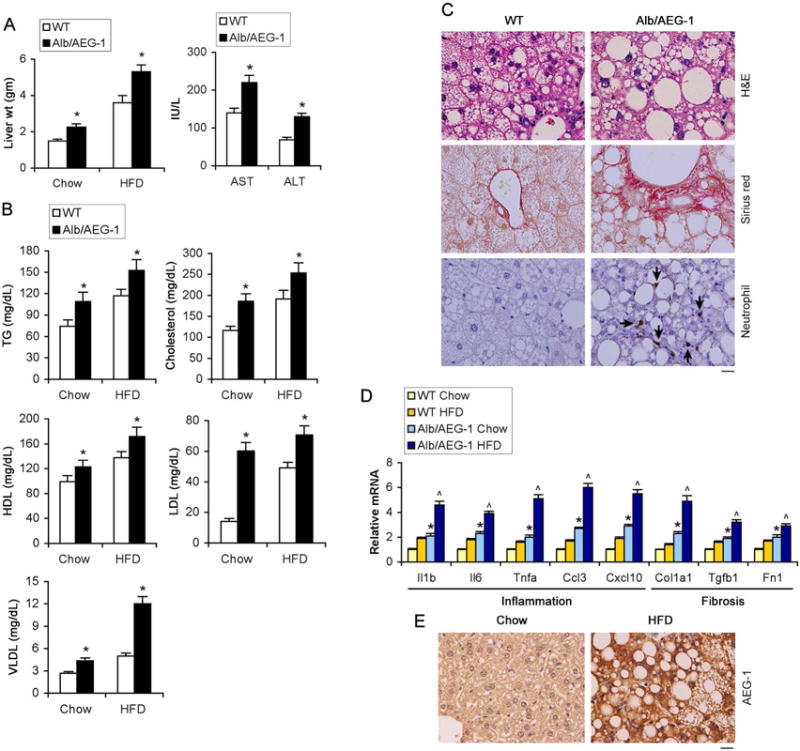
High fat diet (HFD) exacerbates phenotypes of Alb/AEG-1 mice. WT and Alb/AEG-1 littermates were fed HFD for 20 weeks. WT: n = 12; Alb/AEG-1: n = 14. Liver weight (A, left panel), liver enzymes (A, right panel) and plasma lipid profile (B) in chow- and HFD-fed mice at the end of the experiment. Data represent mean ± SEM. * : p<0.01. C. H&E, picrosirius red and neutrophil (arrows) staining of FFPE sections of livers of mice fed HFD. D. Analysis of the mRNA levels of indicated markers of inflammation and fibrosis in the livers of the indicated mice groups (n = 5/group). Data represent mean ± SEM. *: p<0.01 between chow-fed groups; ˄: p<0.01 between HFD-fed groups. E. AEG-1 immunostaining in FFPE sections of livers of WT mice fed chow or HFD. C–D: representative images; magnification 400×; scale bar: 20 μm.
