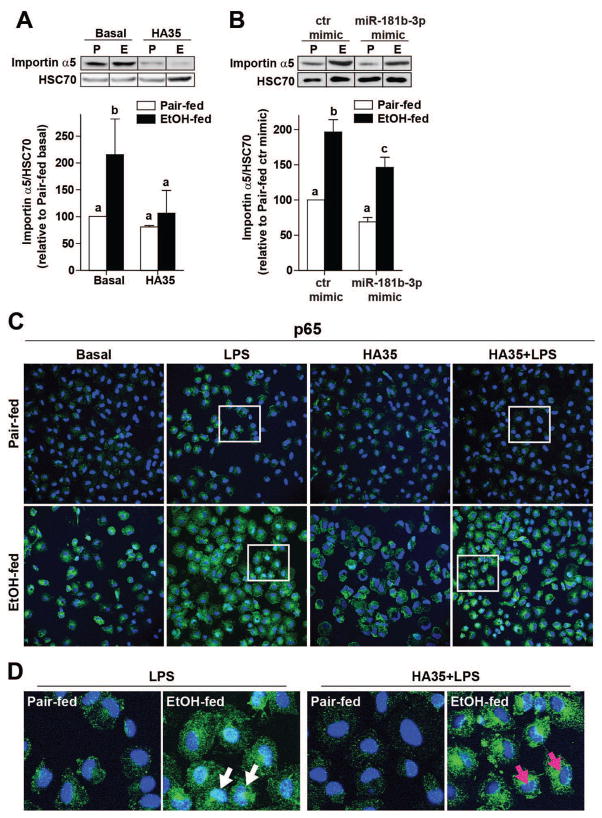
Figure 3. Regulation of importin α5 expression by ethanol and miR181b-3p impacts the nuclear translocation of the p65 subunit of NFκB in primary Kupffer cells.
Kupffer cells isolated from ethanol- and pair-fed rats were (A) treated with 100μg/ml HA35 for 5 h or (B) nucleofected for 18 h with either control miRNA mimic or miR181b-3p mimic. (A/B) Kupffer cells were lysed and importin α5 expression measured by Western blot. HSC70 was used as a loading control. Images were cropped for representational purposes. n=4 independent Kupffer cell isolations. (C) The subcellular localization of p65 subunit of NFκB was assessed by confocal microscopy. Kupffer cells isolated from ethanol- and pair-fed rats were treated or not with HA35 for 5 h and then challenged with 10ng/ml LPS for 30 min. Cells were labeled with antibody to p65 and nuclei visualized with DAPI. (D) Zoomed images at the bottom of the panel illustrate Kupffer cells treated with LPS. White arrows point to p65 co-localized with DAPI and magenta arrows show nuclei only stained with DAPI. Images are representative of 4 independent Kupffer cell isolations.