Fig. 2.
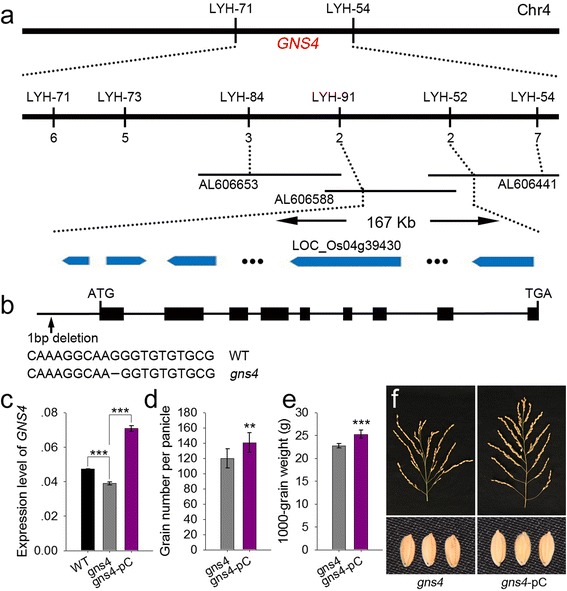
Map-based cloning of GNS4. a Fine mapping of GNS4. GNS4 was primarily mapped between markers LYH-54 and LYH-71 on chromosome 4. Then, GNS4 was fine mapped into a 167-kb segment between markers LYH-52 and LYH-91, using 856 recessive plants from the segregating population. The numbers underneath each marker indicate the numbers of recombinants between GNS4 and the molecular markers. The candidate genes within this region were showed in blue. b Gene structure and the sequence variance of GNS4 between WT and the gns4 mutant. c The expression levels of GNS4 among WT, gns4 and the complementary transgenic plants. The expression level of the rice Actin gene was amplified as a control. Values are means ± s.e. of three independent experiments. d Comparison of grain number per panicle between gns4 mutant and complementary transgenic plants. Data are given as means ± s.e. (n = 11). e Comparison of grain weight between gns4 mutant and complementary transgenic plants. Data are given as means ± s.e. (n = 11). f Panicle and grain phenotypes of gns4 and complementary transgenic plants. gns4-pC presents the transgenic gns4 plants with pGNS4::GNS4ZH11C construct. Significant at ***0.1% and **1%
