Figure 1.
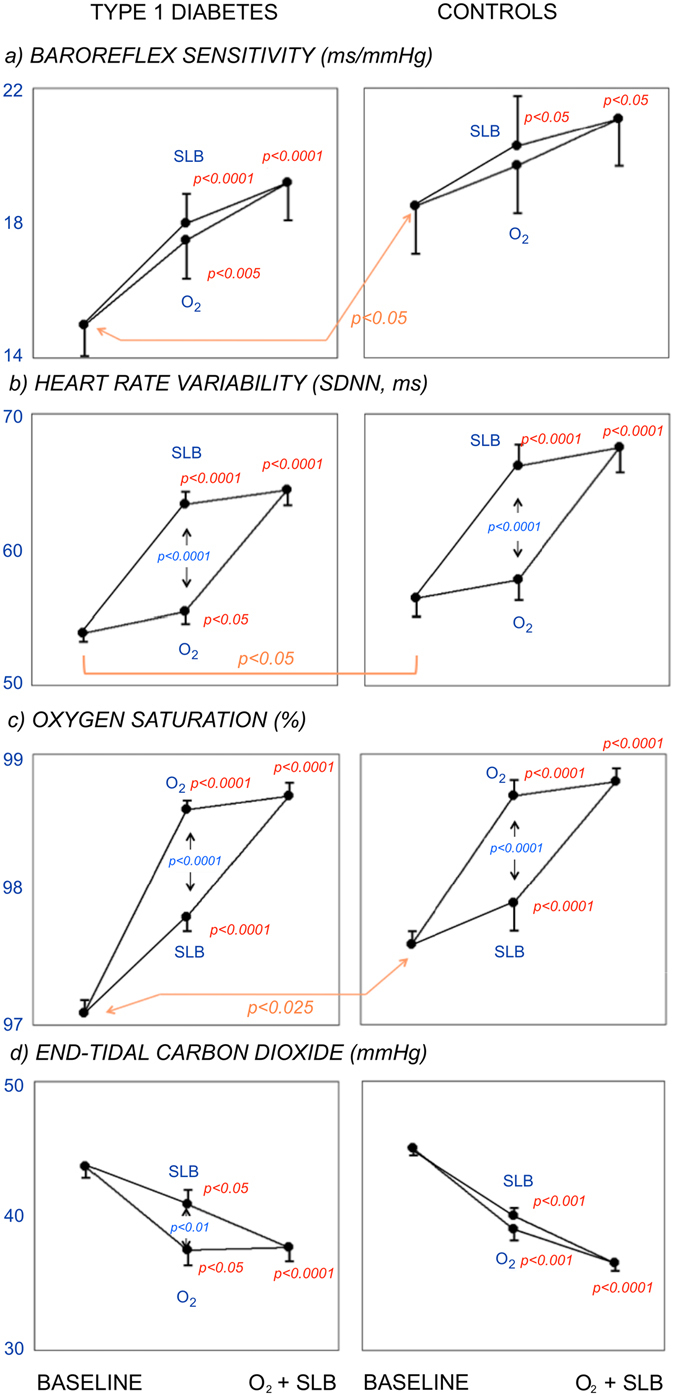
Effect of Slow Breathing (SLB) and Oxygen (O2), alone (middle data of each panel) and combined (right data in each panel) on autonomic function: baroreflex sensitivity (panels a) and heart rate variability (standard deviation of RR intervals, SDNN, panels b), and blood gases: oxygen saturation (panels c) and end-tidal carbon dioxide (CO2-et, panels d). Data from Type 1 diabetic (left panels) and control participants (right panels). Baseline: spontaneous breathing in room air. Within each panel, significances written in red refer to baseline, significances in blue refer to SLB vs O2. Note the additive effect of oxygen and slow breathing in all autonomic and respiratory variables.
