Figure 3.
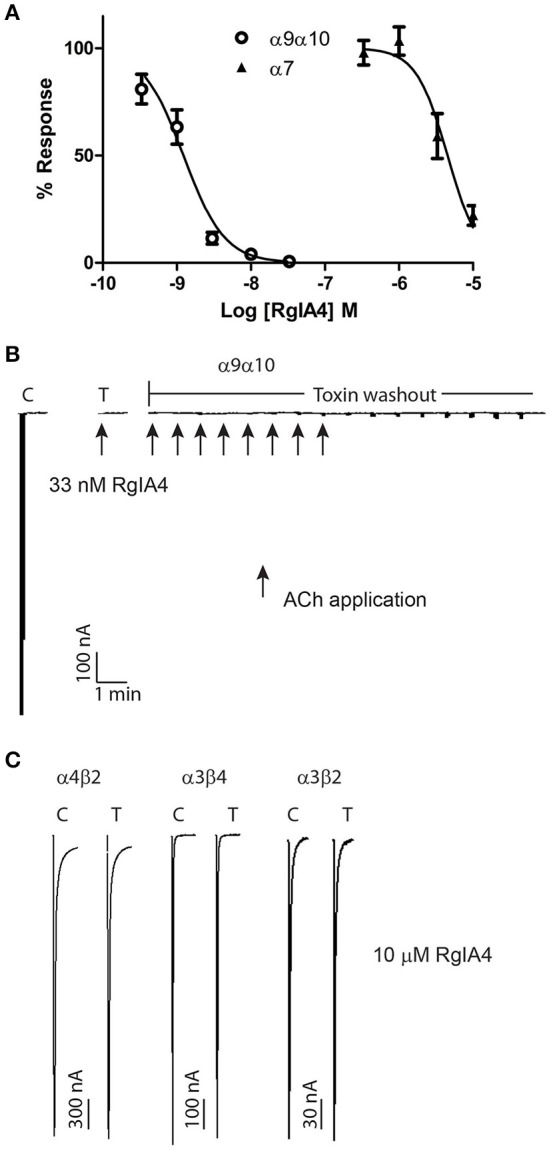
RgIA4 selectively blocks mouse α9α10 nAChRs. nAChRs were expressed in Xenopus laevis oocytes. (A) The concentration response curves for α9α10 and α7 are shown. The IC50 for α9α10 was 1.2 (0.95–1.6) nM with a Hill slope of 1.6 (0.91–2.2). The IC50 for α7 was 4.5 (3.1–6.4) μM with a Hill slope of 2.0 (0.84–3.2). The values in parenthesis denote the 95% confidence intervals; n = 3–7 for each condition. (B) Recovery from toxin block of α9α10 is relatively slow. Example trace of block by 33 nM RgIA4. Recovery after 15 min toxin washout was ~2%. Arrows indicate application of 10 μM ACh. (C) At all other indicated nAChR subtypes, RgIA4 (10 μM) blocked less than 50% of the ACh-evoked response; the percent of the ACh-response for each subtype was α1β1δϵ, 95.0 ± 3.8; α1β1δγ, 86.2 ± 3.8; α3β2, 106 ± 2.9; α3β4, 105 ± 0.7; α4β2, 102 ± 3.3; α4β4, 74.3 ± 3.0. n = 3–4 for each condition; ± is S.E.M. Example traces for α4β2, α3β4, and α3β2 are shown. Results are summarized in Table 1.
