Figure 4.
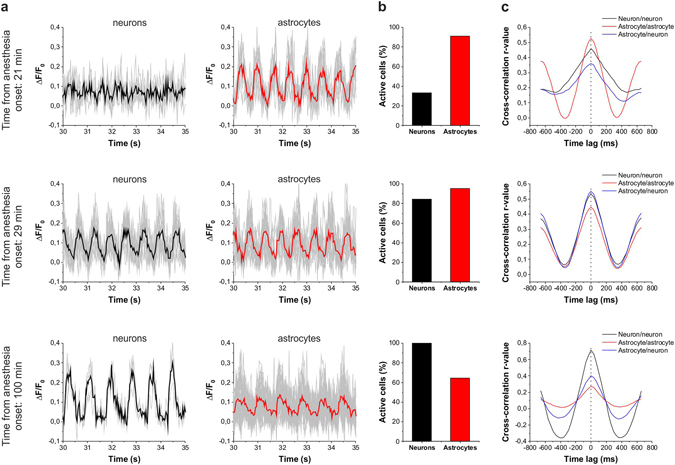
Astrocytes are more broadly involved in SWA than neurons in the early stage of ketamine/xylazine anesthesia. (A–C) Changes in the involvement of neurons and astrocytes in the network activity during SWA under ketamine-xylazine anesthesia after 21 min, 29 min and 100 min from the onset of anesthesia. (A) Fluorescent intensity changes detected in neurons and SR101-identified astrocytes. Individual Ca2+ traces (gray) and their averages in neurons (black) and astrocytes (red) are shown on 5-sec segments of the imaging sessions at each time point. (B) The ratio of neurons (black) and astrocytes (red) showing repetitive Ca2+ transients in percentage of all astrocytes or neurons, respectively, in the field of view in this particular imaging session. (C) Cross-correlation of neuron/neuron (black), astrocyte/astrocyte (red) and astrocytes/neuron (blue) pairs of active cells (n = 12–420 cell pairs). All data were recorded from the V1 area of a P78 rat.
