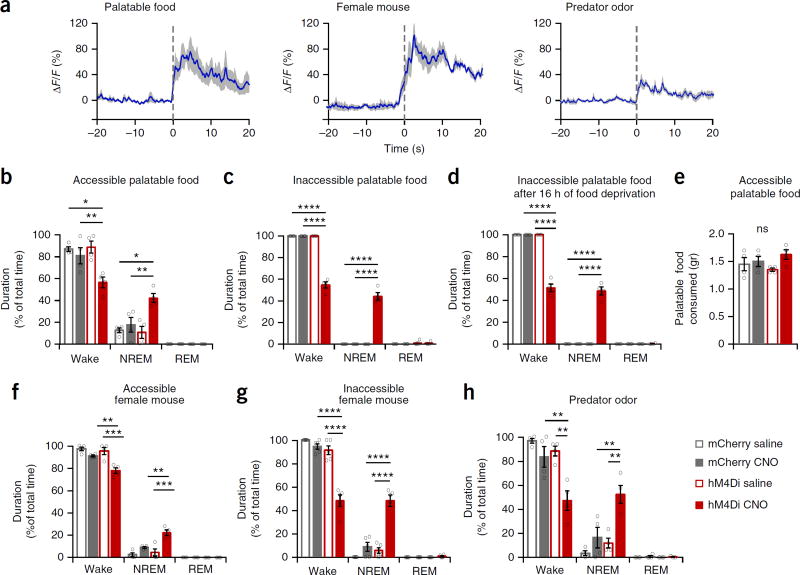
Figure 3.
Activity in Th+ VTA neurons is necessary for wake maintenance even in the face of salient stimuli, (a) Th+ VTA neurons population activity in response to salient stimuli. Time 0 represents contact with food or predator odor and the placement of the female mouse in the cage. Presented are average responses (n = 4 mice; blue trace) ± s.e.m. (gray shading). (b-d,f-h) Percent time in wake, NREM and REM sleep (mean ± s.e.m.; n = 4 per group for b-d,f,h and n = 5 for g; two-way RM ANOVA between compound injected and viral transduction, followed by Sidak’s post hoc test; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001. (b) In the presence of high-fat chow (interaction: F1,6 = 6.75 (wake) and 7.58 (NREM), P= 0.04 (wake) and 0.03 (NREM)). (c,d) In the presence of inaccessible high-fat chow (c) in normally fed mice (interaction: F1,6 = 241.3 (wake) and 162.1 (NREM), P= 4.5 × 10−6 (wake) and 1.4 × 10−5 (NREM)) and (d) in 16-h food-deprived mice (interaction: F1,6 = 193.1 (wake) and 173.1 (NREM), P= 8.65 × 10−6 (wake) and 1.9 × 10−5 (NREM)). (e) Amount (mean ± s.e.m.) of high-fat chow consumed during a 1-h test period in the presence of 6 g high-fat chow (interaction: F1,6 = 1.45, P= 0.27). (f) In the presence of a freely moving female mouse (interaction: F1,6 = 12.31 (wake) and 12.56 (NREM), P= 0.01 for wake and NREM)). (g) In the presence of an inaccessible female mouse (interaction: F1,8 = 50.22 (wake) and 34.97 (NREM), P= 0.0001 (wake) and 3.5 × 10−4 (NREM)). (h) In the presence of a predator odor (virus: F1,6 = 13.9 (wake) and 14.75 (NREM), P= 0.0098 (wake) and 0.0086 (NREM); compound injected: F1,6 = 16.9 (wake) and 17.47 (NREM), P= 0.0063 (wake) and 0.0058 (NREM)).