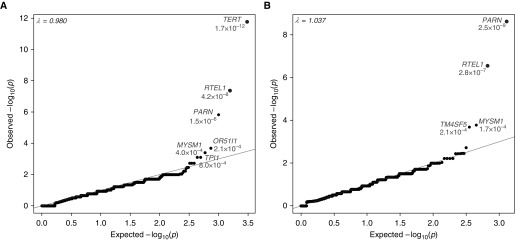
Figure 1.
Quantile–quantile plot of pulmonary fibrosis collapsing analyses. Results are shown for the analysis of 262 pulmonary fibrosis case and 4,141 control subjects. (A) A total of 15,393 genes had at least one case or control carrier. Qualifying variants have a minor allele frequency less than 0.05% in the test cohort and are absent among external reference cohorts. Variants are annotated as loss-of-function, in-frame indel, or missense predicted to be “probably damaging” by Polymorphism Phenotyping version 2 (HumDiv). Two genes, TERT and RTEL1, achieved study-wide significance (adjusted α = [0.05/(6 × 18668)] = 4.46 × 10−7). (B) A total of 10,710 genes had at least one loss-of-function case or control carrier. Qualifying variants are variants with a population minor allele frequency less than or equal to 0.1% and are annotated as loss-of-function single-nucleotide variants or indels. PARN and RTEL1 achieved study-wide significance (P < 4.46 × 10−7).