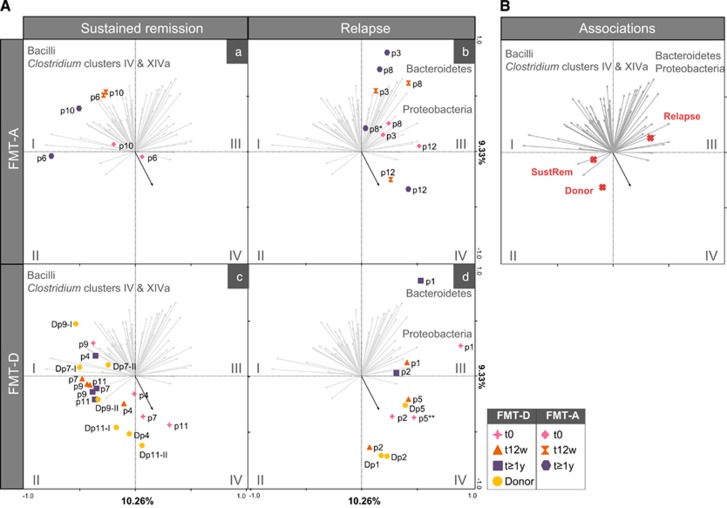
Figure 2.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of samples at t0, t12w and t1 year. Grey arrows represent the 65 best-fitting genus-like bacterial groups, shown grouped into their corresponding phyla (Bacteroides and Proteobacteria) and orders belonging to the Firmicutes phylum (Bacilli, Clostridium clusters IV and XIVa) (detailed information of bacterial groups associated with quadrants I–IV in Supplementary Table 3). Blue arrow in quadrant IV indicates R. gnavus. Twenty per cent of the variation in the data set is explained in the first two axes. (A) Samples are divided into FMT-A with sustained remission (a) and relapse (b) and FMT-D with sustained remission (c) and relapse (d) and their corresponding donors (of first or second FMT, shown as I or II). (B) Red crosses show association of explanatory variable ‘Sustained Remission’ (which includes group relapse, sustained remission and donors) with samples and bacterial groups. *Patient 8 includes two samples after 1 year. **⩾1- year sample from Patient 5 did not fulfil the quality control criteria of the HITChip pipeline.