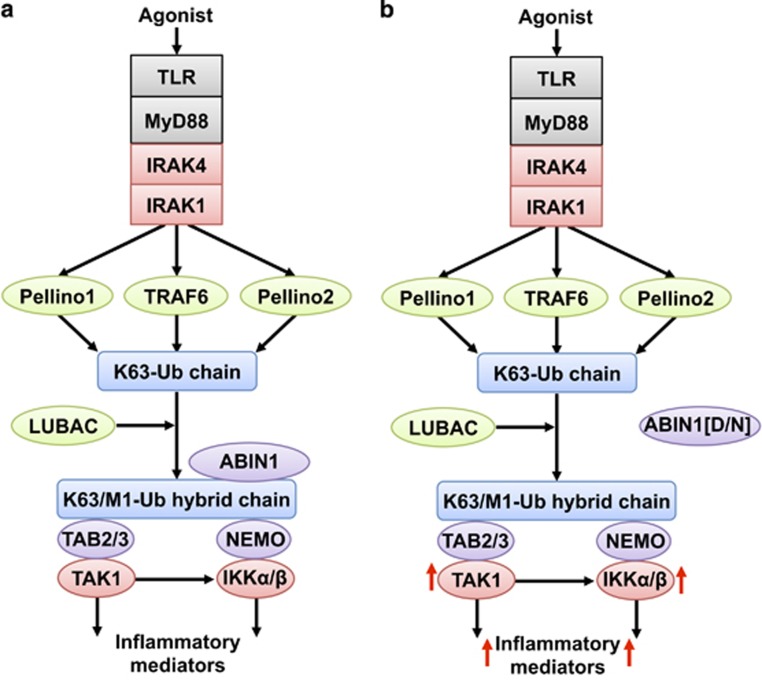
Figure 4.
ABIN1 restricts the activation of TAK1 and the canonical IKK complex. (a) ABIN1 binds to K63/M1-Ub hybrids and competes with the TAK1 and IKK complexes for binding to these ubiquitin chains. This suppresses the interaction of the TAK1 and IKK complexes with these ubiquitin chains, restricting their activation and the production of inflammatory mediators. (b) In dendritic cells and B cells from knock-in mice expressing the ubiquitin-binding-defective ABIN1[D485N] mutant, this restriction is removed, leading to hyperactivation of the TAK1 and IKK complexes and the overproduction of inflammatory mediators (red arrows). This leads to the spontaneous development of SLE when the ABIN1[D485N] mice are 4–5 months old. The colour key is as in Figures 1 and 3