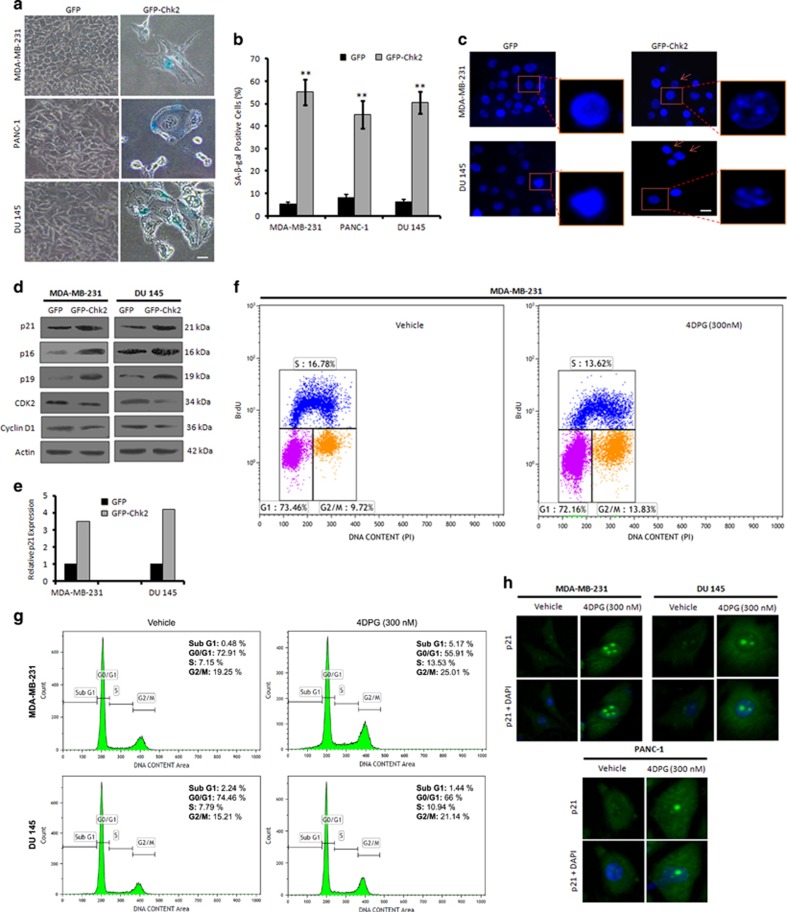
Figure 4.
Chk2 induction promotes premature senescence in p53-mutated invasive cancer cells. (a) MDA-MB-231, PANC-1 and DU 145 cells were transfected with GFP and GFP-Chk2 construct; 72 h of post transfection, cells were incubated with X-gal staining solution for 48 h and then checked for the SA-β-gal activity of the cells. Images were captured under bright-field microscope at × 20 magnification. Scale bar: 20 μm. (b) Bar graph indicates quantification of SA-β-gal-positive cells (n=3, error bars indicate±S.D.). **P<0.01. (c) MDA-MB-231 and DU 145 cells after transfection with GFP and GFP-Chk2 construct for 72 h, stained with DAPI containing mounting media and observed for the SAHF under Floid Cell Imaging Station at × 20 magnification. Scale bar: 20 μm. Enlarged scale-up images to properly show the formation of heterochromatin foci. (d) Seventy-two hours of post transfection with GFP and GFP-Chk2, whole-cell lysates were prepared and subjected to western blot analysis of the various senescence specific markers like; p21, p16, p19, CDK2 and cyclin D1. (e) Bar graph showing relative p21 expression from densitometric analysis of the obtained bands from the western blotting experiment. (f) MDA-MB-231 cells were treated with 4DPG (300 nM) for 48–72 h and then pulse labeled with BrdU (30 μM) for 1 h. Cells were then processed for BrdU flow cytometric analysis. (g) Cells were treated with 4DPG (300 nM) along with vehicle for 72 h and checked for cell cycle analysis (PI staining) through flow cytometry. (h) MDA-MB-231, PANC-1 and DU 145 cells were treated with 4DPG (300 nM) along with vehicle and employed for the immunocytochemical analysis of p21 localization (original magnification × 20)