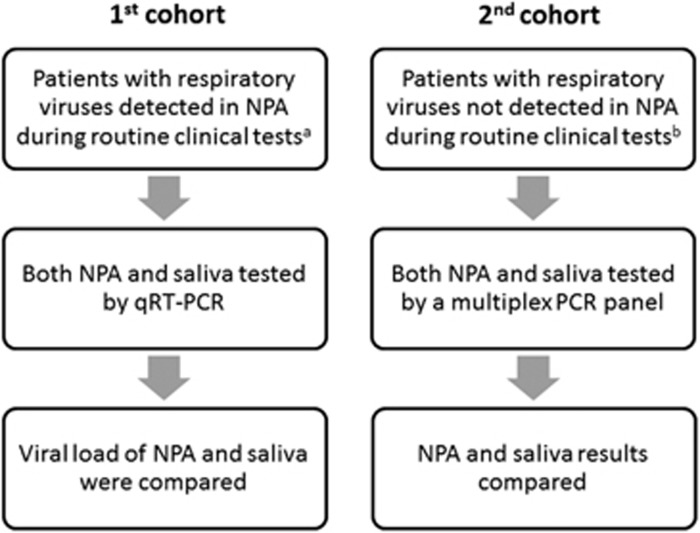
Figure 1.
Study design. nasopharyngeal aspirate, NPA; quantitative PCR with reverse transcription, qRT-PCR. aRoutine clinical testing was performed using antigen detection by the DFA, which included the influenza A and B viruses, parainfluenza virus types 1–3, respiratory syncytial virus, human metapneumovirus and adenovirus. From 1 March to 8 April 2015 (during the peak influenza A virus season), monoplex real-time RT-PCR for the influenza A M gene was performed for patients admitted to the general medical ward. bPatients whose NPA specimens either tested negative for respiratory viruses by DFA or had insufficient NPCs for DFA during routine clinical testing. Insufficient NPCs is defined as <20 NPCs in the entire well.