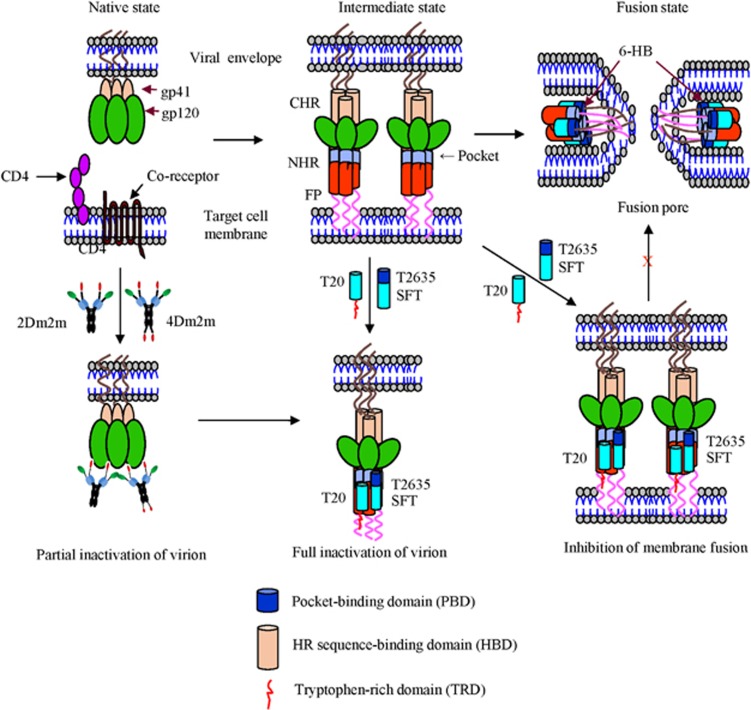
Figure 3.
Putative mechanisms of action of bispecific proteins and/or HIV-1 fusion inhibitory peptides to inactivate virions and inhibit viral fusion and entry. 2Dm2m or 4Dm2m binds to gp120 via its mD1.22 and m36.4 domains, resulting in the partial inactivation of the virion. Binding of 2Dm2m or 4Dm2m to gp120 induces the exposure of the gp41 trimer, to which the HIV-1 fusion inhibitory peptide, T20, T2635 or SFT, binds, leading to the full inactivation of the virion. The T20, T2635 or SFT peptide can also bind to the exposed gp41 trimer induced by CD4 on the target cell, causing inhibition of viral–cell membrane fusion. Sifuvirtide, SFT.