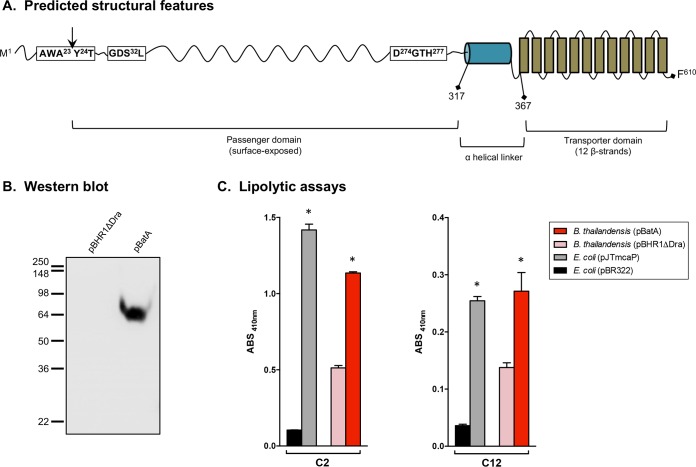
FIG 1.
Selected characteristics of the batA gene product and constitutive expression by recombinant B. thailandensis bacteria. (A) Different regions of the predicted BatA protein with positions of residues defining selected domains. The vertical arrow indicates the predicted signal sequence cleavage site. (B) Proteins were extracted from B. thailandensis DW503 bacteria carrying the plasmids pBHR1ΔDra (control) and pBatA (specifying the WT batA gene product) and analyzed by Western blotting with the monoclonal antibody BatA-MAb 1. Molecular mass markers are shown on the left in kilodaltons. (C) Freshly plate-grown bacteria were suspended in PBS, and equivalent numbers of cells were incubated with pNPs composed of 2 (C2) to 18 (C18) carbon chains. The absorbance (ABS) of triplicate samples was measured at a wavelength of 410 nm. The results are expressed as mean absorbances of samples and standard errors. Substrates were tested on at least 3 separate occasions. The asterisks indicate that recombinant bacteria producing BatA and McaP exhibited lipolytic activity levels significantly greater than those of their corresponding controls (P < 0.005; Mann-Whitney test). Data from representative experiments are shown. Only the substrates cleaved by BatA are shown (C2 and C12). The AT did not exhibit significant lipolytic activity toward pNP C4, C6, C8, C10, C14, C16, or C18.