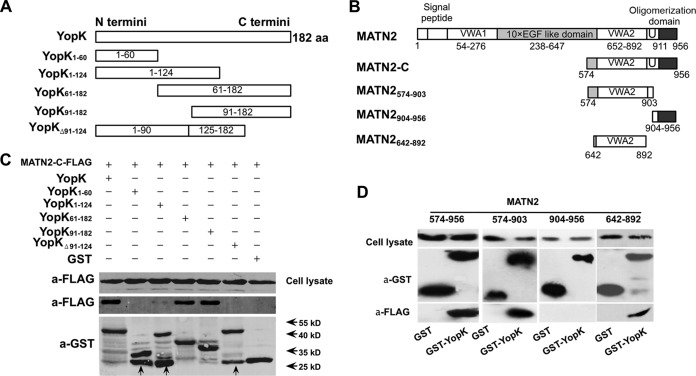
FIG 1.
Amino acid residues 91 to 124 of YopK are critical for MATN2 binding. (A) Schematic diagrams of various YopK truncations. (B) Schematic diagrams of human MATN2 truncations. (C) A GST pulldown assay was used to identify the amino acids that are critical for the binding of YopK to MATN2. Arrows indicate the bands of degradation products or protein impurities. (D) Binding between GST-YopK and the MATN2 truncations was analyzed by GST pulldown assay. GST-tagged YopK or YopK truncations expressed in E. coli were bound to glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids expressing MATN2 truncations. After 48 h of transfection, cells were lysed and stored at −80°C until use. Sepharose 4B beads bound with purified GST-tagged YopK or YopK truncations were incubated with cell lysates containing MATN2 or its truncations. The beads were thoroughly washed to remove the unbound proteins. Bound proteins were then eluted by boiling in sample buffer and separated by SDS-PAGE. Proteins were transferred onto a PVDF membrane and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-FLAG or anti-GST antibodies.