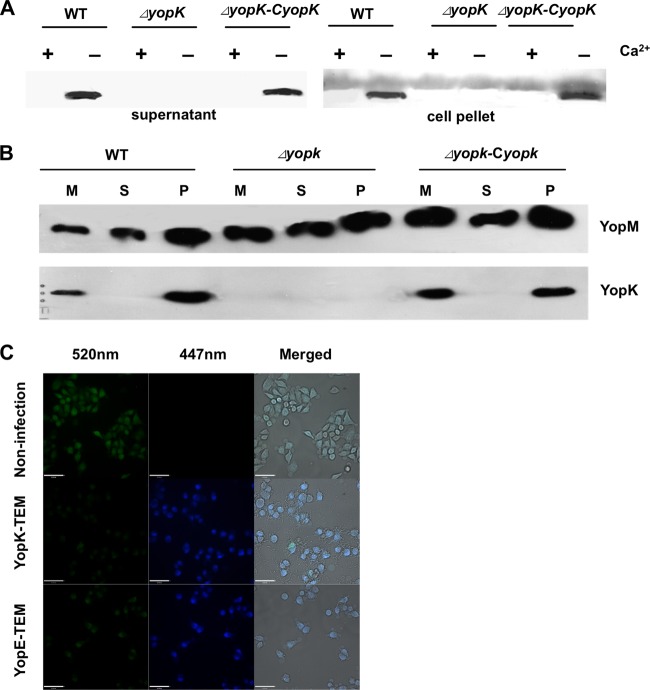
FIG 2.
YopK secreted by Y. pestis is abundantly present in culture medium of infected HeLa cells. (A) Expression and secretion of YopK by different Y. pestis strains were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-YopK antibody. The wild-type, ΔyopK, and ΔyopK-CyopK Y. pestis strains were cultured in TMH medium at 37°C with or without calcium as indicated. Secreted proteins in the culture supernatant and bacterial cell pellets were separated by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-YopK antibody. (B) Translocation of YopK into HeLa cells was analyzed by immunoblot detection of cell fractions using anti-YopK antibody. HeLa cells were infected with the indicated strains, and the culture medium (M) was collected after 2 h of infection. The infected cells were then lysed in 0.1% Triton X-100 and centrifuged to separate the supernatants (S) and cell pellets (P). Proteins in different cell fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting using anti-YopK antibody. At least three independent experiments were performed, and a representative result is shown. (C) Translocation of YopK into HeLa cells was analyzed using a BlaTEM reporter. HeLa cells were infected with Y. pestis strains harboring pBBR1-yopE-TEM or pBBR1-yopK-TEM for 1 h. Cells were then loaded with 1 μg ml−1 CCF2-AM substrate solution. Cell images were taken using an UltraVIEW Vox live-cell imaging system with an emission wavelength of 409 nm and detection wavelengths of 447 and 520 nm. All the scale bars represent 62 μm.