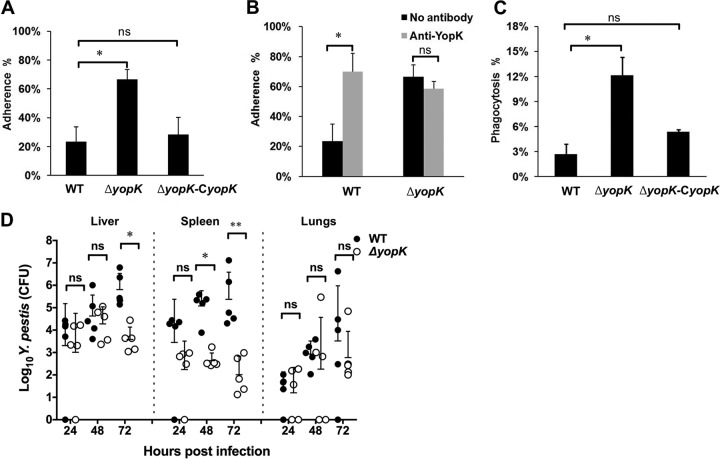
FIG 3.
YopK inhibits bacterial adhesion to host cells and promotes resistance to phagocytosis by RAW264.7 cells. (A) HeLa cells were infected with the wild-type, ΔyopK, or ΔyopK-CyopK Y. pestis strain at an MOI of 100, and 1 μM cytochalasin D was added to inhibit the endocytosis of HeLa cells. After 2 h of infection, cells were extensively washed in prewarmed PBS to remove unattached bacteria and then lysed in 0.1% Triton X-100. The number of bacteria that adhered to the HeLa cells was counted by plating cell lysate dilutions on agar plates. The percentage of adhesion was calculated by dividing the number of attached bacteria by the total number of bacteria in the well. (B) HeLa cells were infected with the wild-type or ΔyopK Y. pestis strain as described for panel A except that anti-YopK antibody at 100 μg ml−1 was present in the culture medium. The percentage of adhesion was calculated as described above. (C) RAW264.7 cells were infected with the indicated Y. pestis strains at an MOI of 20, and gentamicin was added into the culture medium after 0.5 h to kill the extracellular bacteria. Phagocytosed bacterial cells were counted by plating the diluted RAW264.7 cell lysates as described for panel A. All experiments were independently performed at least three times in triplicate. Statistical analysis was performed with GraphPad Prism version 6.0c for Mac using one-way ANOVA with Dunnett's multiple-comparison tests to analyze the significance of differences in bacterial adhesion or phagocytosis between the different strains. (D) Groups of mice (n = 5 for each group) were infected with ∼100 CFU of wild-type or ΔyopK Y. pestis via i.v. injection. Mice were sacrificed at the indicated times, and the tissues were homogenized. The bacterial loads were measured by plating dilutions of homogenates on agar plates. Colonization of the ΔyopK mutant in spleen was greatly hampered at 48 and 72 hpi. In liver, the difference was significant only at 72 h. The significance of the differences between the mice infected with the wild-type and ΔyopK strains was determined by multiple t tests (**, P < 0.01; *, P < 0.05; ns, not significant).