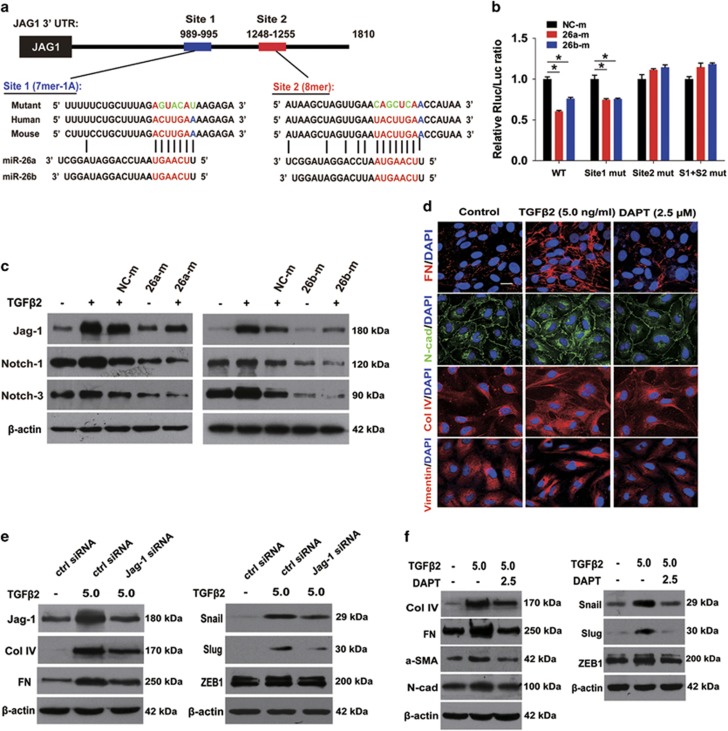
Figure 4.
MiR-26a and -26b inhibit LEC–EMT via directly targeting Jagged-1/Notch signaling, and Jagged-1 siRNA and Notch pathway specific inhibitor DAPT reverse LEC–EMT in vitro. (a) Predicted miR-26a and -26b target two sites of potential-binding sequences in Jagged-1-3′UTR and mutants containing four mutated nucleotides (green) in two sites of Jagged-1-3′UTR, respectively. (b) Normalized luciferase activities of reporters containing wild-type or mutant 3′-UTR of Jagged-1 in 293 T cells co-transfected with miRNA negative control mimic (NC-m), miR-26a mimic (26a-m) or miR-26b mimic (26b-m). *P<0.05. (c) Western blot analysis of Jagged-1, Notch-1 and Notch-3 protein levels in LECs transfected with miRNA negative control mimic, miR-26a mimic or miR-26b mimic, and treated with TGFβ2 (5 ng/ml) for 48 h. (d) Immunofluorescent staining analysis of EMT markers FN, N-cadherin, Col IV and vimentin in LECs transfected and treated as indicated in c. Scale bar, 40 μm. (e) Western blot analysis of Jagged-1, Col IV, FN, Snail, Slug and ZEB1 protein levels in LECs transfected with control siRNA, or Jagged-1 siRNA, and treated with TGFβ2 (5 ng/ml) for 48 h. (f) Western blot analysis of Col IV, FN, α-SMA, N-cadherin, Snail, Slug and ZEB1 protein levels in LECs exposure to TGFβ2 with or without DAPT (2.5 μM) for 48 h