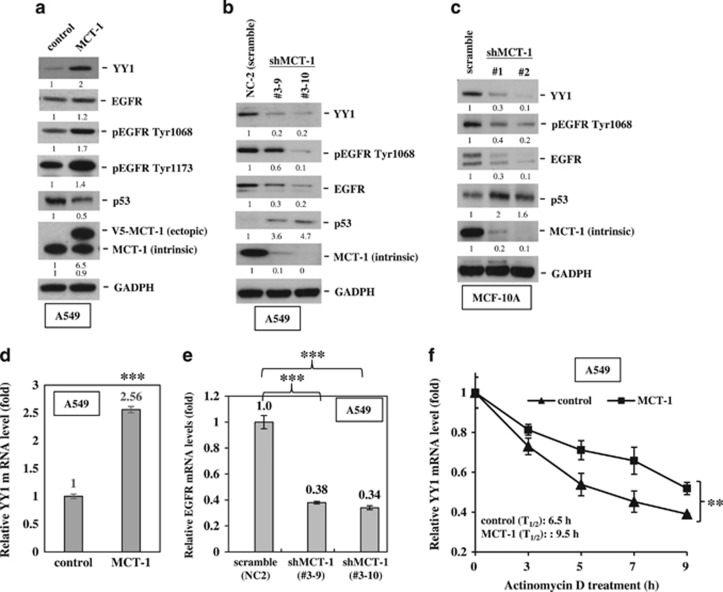
Figure 1.
Overexpression of MCT-1 promotes YY1-EGFR signaling. MCF-10A cells and A549 cells overexpressing V5-tagged MCT-1 (V5-MCT-1) or with depleted endogenous MCT-1 (shMCT-1) and their comparative controls were analyzed. (a) The expression of YY1, EGFR and p53 was evaluated when A549 cells were starved for 24 h and then stimulated by EGF (20 ng/ml) and insulin (10 μg/ml) for 1 h. (b) Two different clones (#3–9 and #3–10) of MCT-1 knockdown and scrambled knockdown (NC2) in A549 cells were analyzed for YY1, EGFR and p53 expression upon EGF/insulin stimulation for 1 h. (c) MCF-10A cells with different degrees of MCT-1 knockdown (clone #1 and #2) and scrambled knockdown were examined after starvation for 24 h followed by EGF/insulin stimulation for 1 h. The protein amounts were normalized to GAPDH, and the phosphorylated EGFR levels were normalized to total EGFR before comparison with the comparative controls. (d) YY1 mRNA levels were surveyed in the A549 cells with different MCT-1 levels. (e) Relative EGFR mRNA levels were quantified in different A549 lines with MCT-1 knockdown (#3–9 and #3–10) and in A549 cells with scrambled knockdown vector (NC2). (f) The half-life (T1/2) of YY1 mRNA was examined in A549 cells after actinomycin D treatment. The data represent the mean±s.d. (n=3). **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001.