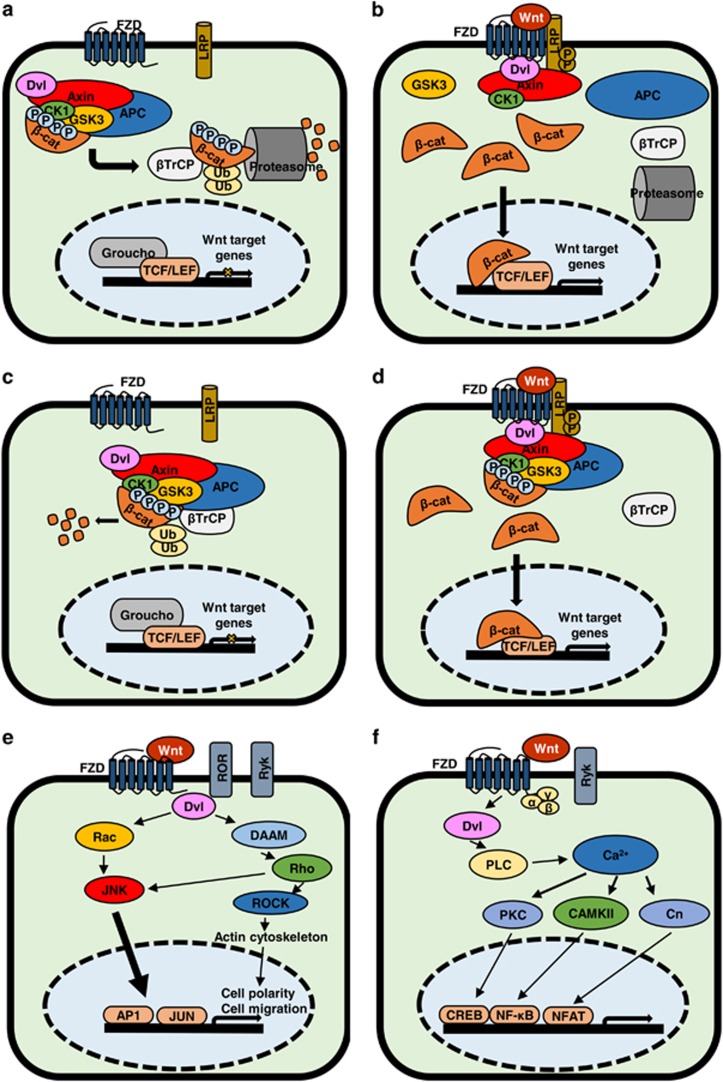
Figure 1.
Classical and new Wnt/β-catenin pathway canonical and non-canonical pathways. (a) Overview of the ‘classical’ model of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in OFF state with no ligand bound to FZD receptor. (b) Overview of the ‘classical’ model of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in ON state where Wnt ligand is bound to FZD receptor. (c) Overview of ‘new’ model of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in OFF state with no ligand bound to FZD receptor. (d) Overview of the ‘new’ model of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in ON state with Wnt ligand bound to FZD receptor. (e) Overview of Wnt planar cell polarity (PCP) pathway in ON state. Wnt binds multiple receptors including FZD and co-receptors ROR and Ryk. This activates Rho and Rac, which activate ROCK and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), respectively, leading to actin polymerization and regulates cytoskeletal arrangements. (f) Overview of Wnt/Ca2+ pathway in ON state. Wnt is able to bind FZD, Ryk to initiate signal transduction, which is effected through Dvl and G proteins (α, β, γ). Gene transcription is induced through proteins PKC, CaMKII and Cn (Calcineurin)-activating transcription factors.