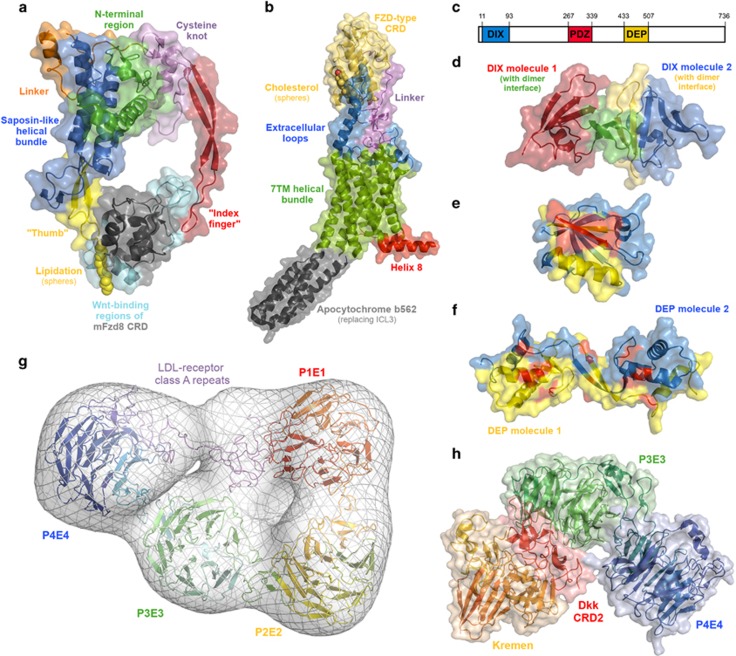
Figure 2.
Molecular structures of the key Wnt signaling proteins and interactions. (a) X-ray crystal structure of the Xenopus Wnt8 complex with the mouse FZD8 cysteine-rich domain (PDB 4F0A). The key structural regions of the Wnt fold are highlighted, as are the major Wnt-interacting regions of the CRD. (b) X-ray crystal structure of the Smoothened receptor (PDB 5L7D), a Class F G protein-coupled receptor, related to FZD. The key structural regions of Smo are highlighted, as well as helix 8, which is of relevance for Dishevelled binding by FZD. (c) Schematic representation of the location of the DIX, PDZ and DEP domains within Dvl. (d) X-ray crystal structure of the DIX homodimer (PDB 4WIP). (e) X-ray crystal structure of the PDZ domain bound to a peptide (red; PDB 3CBX). The peptide-binding site is shown in yellow. (f) X-ray crystal structure of a DEP homodimer (PDB 5LNP), highlighting residues known to affect Wnt signaling (shown in red). (g) Model of the LRP6 ectodomain generated by molecular dynamics flexible fitting of the crystal structures of the P1E1–P2E2 domains (PDB 3S94) and P3E3–P4E4 domains (PDB 4A0P), and a homology model of the LDL-R type A domains (generated in Prime, based on the crystal structure of the LDL receptor ectodomain (PDB 1N7D)) to the electron microscopy structure (EMDatabank accession 1964). Gaps in the crystal structures and between the various components modeled using Prime. (h) X-ray crystal structure complex of the cysteine-rich domain 2 of Dickkopf with Kremen and the LRP6 P3E4–P4E4 domains (PDB 5FWW).