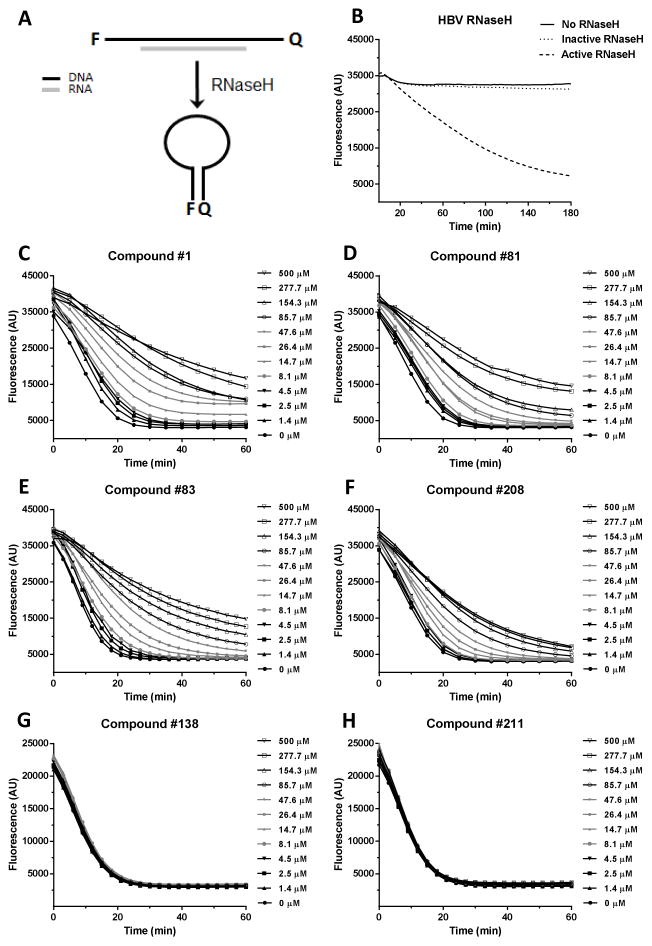
Figure 2. Effects of the compounds on purified HBV RNaseH.
(Panel A) HBV RNaseH inhibition was determined using a molecular beacon RNaseH assay in which quenching of fluorescence from the RNaseH substrate is measured following removal of the RNA strand by the RNaseH, causing the folding of the DNA strand into a hairpin. (Panel B) Activity of wild-type and an active site knockout mutant (D702A/E731A) HBV RNaseHs. (Panels C to H) Fluorescence intensity from representative RNaseH reactions incubated for 60 min. in the presence of 0 to 500 μM of compounds #1, 81, 83, 138, 208, and 211.