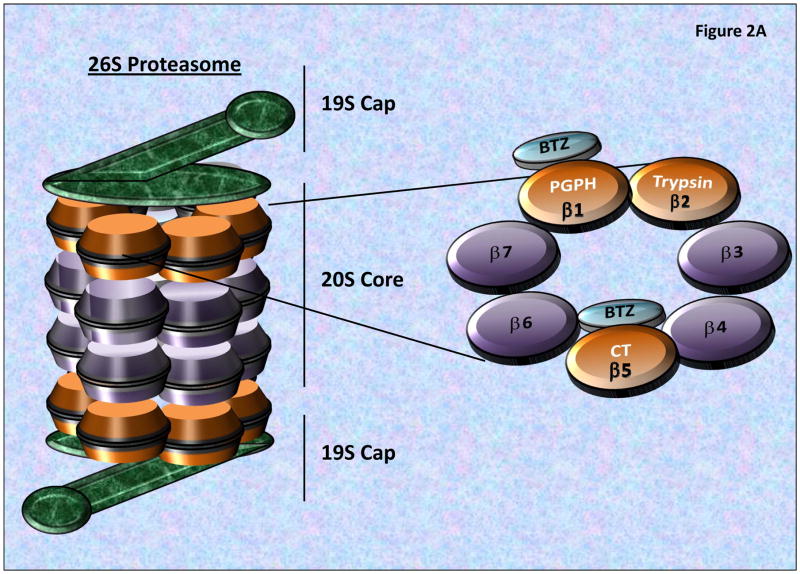
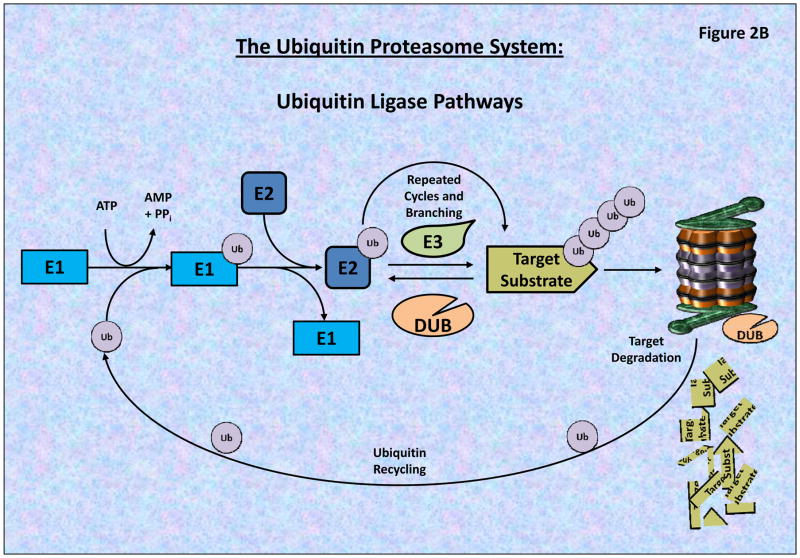
Figure 2. The 26S Proteasome Structure and Proteolytic Activities.
A) The 26S proteasome consists of a 20S catalytic core and two 19S regulatory caps, which removes/recycles linked Ub, linearize and direct targeted proteins into the 20S Core. The 20S core is composed of 2-inner β-rings and 2-outer α-rings. As seen the β-rings contain 3 proteolytic sites (β1, β2 and β5 subunits), possessing post-glutamyl peptide hydrolase-like (PGPH) (or caspase-like), trypsin-like, or chymotrypsin-like (CT) activities, respectively. BTZ primarily binds to the β5 and β1 subunits blocking proteasome activities. B) The Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) is composed of a series of ubiquitinating enzymes which work through the specific and targeted addition and branching of Ubiquitin to proteins which are differentially targeted by different E3-Ligases (which possess target specificity). Through the utilization of ATP, Ub is conjugated to the E1 Ligase, and then transferred to an E2 Ligases which subsequently transfers the Ub Moiety to a target protein or an existing Ub-chain. The complexity of the Ub branching pattern is determined by the interaction of numerous UPS components including the Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs) which serve to both recycle as well as modulate the branching patterns of ubiquitinated proteins. Most poly-ubiquitinated proteins then pass through the 19S cap which linearizes the peptide and passes it into the 20S Core proteasome for catalytic degradation.