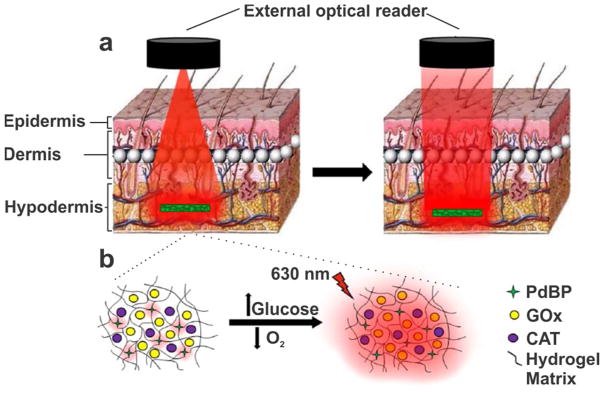
Figure 7.
(a) Hydrogel system as a fully-implantable, optically active glucose sensor. The excitation source ((i); light-emitting diode, l = 630 nm) and detector ((ii); photo-multiplier tube) were housed in a 1.5-in diameter “puck”. (b) The hydrogel sensor was composed of a poly(HEMA)-co-PAM hydrogel matrix containing encapsulated glucose oxidase (GOx), catalase (CAT), and an oxygen-sensitive benzoporphyrin phosphor (PdBP). In the presence of glucose, GOx catalyzes the oxidation of b-D-glucose to D-glucono-1,5-lactone, reducing the oxygen to hydrogen peroxide. Catalase is included as a peroxide scavenger, to increase the lifetime of GOx. Reprinted with permission from Reference 68. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2015, 9 (5), 985–992. Copyright 2015, SAGE Publications.