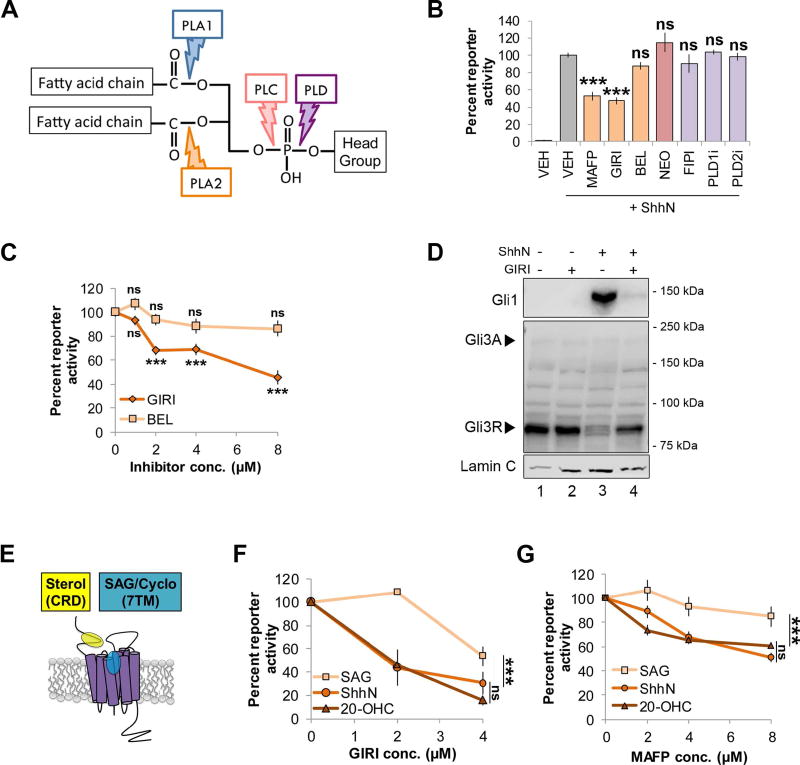
Figure 1.
cPLA2 inhibitors modulate Shh signaling. For all panels, *** indicates p ≤ 0.0001; ns, p > 0.05. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM). A. Schematic of a phospholipid showing phospholipase hydrolysis sites. B. Light2 reporter cells were pretreated with PLA2 inhibitors (MAFP (5 µM), GIRI (5 µM) and BEL (5 µM); orange), PLC inhibitor NEO (200 µM; pink) or PLD inhibitors (FIPI (40 nM), PLD1i (40 nM) and PLD2i (40 nM); purple) prior to stimulation with ShhN conditioned media. Statistical significance was determined using a one-way ANOVA. C. Light2 cells were pretreated with cPLA2 inhibitor (GIRI, diamond) or iPLA2 inhibitor (BEL, square) prior to ShhN conditioned media treatment. Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA. D. NIH3T3 cells were pretreated with GIRI (4 µM) prior to stimulation with ShhN conditioned media. Gli1 and Gli3 protein levels were analyzed in nuclear fractions by western blot. The experiment was performed twice. A representative blot is shown. Arrowheads indicate Gli3 activator and repressor species. Lamin C is the nuclear marker. E. Diagram of Smo ligand binding pockets. F–G. Light2 cells were pretreated with GIRI or MAFP prior to SAG (100 nM, square), 20-OHC (10 µM, triangle) or ShhN conditioned media (circle). Statistical significance was determined using a two-way ANOVA. For all experiments involving Light2 cells, Gli-luciferase reporter activity was normalized to tk-renilla control and expressed relative to the agonist-stimulated control. PL inhibitors were added 2 hours prior to agonist for pretreatment. Assays were repeated a minimum of three times in triplicate and all data pooled.