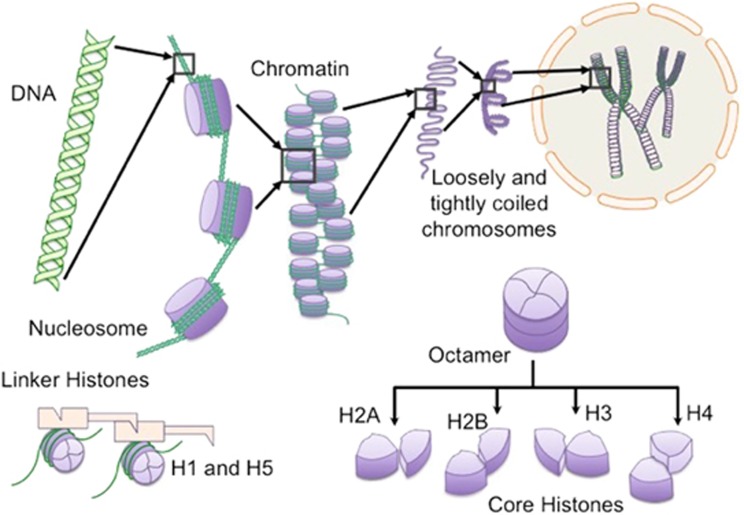
Figure 2.
Intracellular structure and function of histone. Histones are intra-nuclear alkaline proteins that contribute to the structural organisation and stability of chromatin. Individual core histone monomers (H2A, H2B, H3 and H4) combine to form octameric structures. Each octamer is made up of two H3-H4 and two H2A-H2B dimers. DNA strands (146 base pairs) wind around the octamers to form nucleosomes and are held together with linker histones (H1 and H5), forming chromatin. Chromatin coils and condenses to form chromosomes. This enables vast amounts of DNA to be compacted tightly within the nucleus of the cell