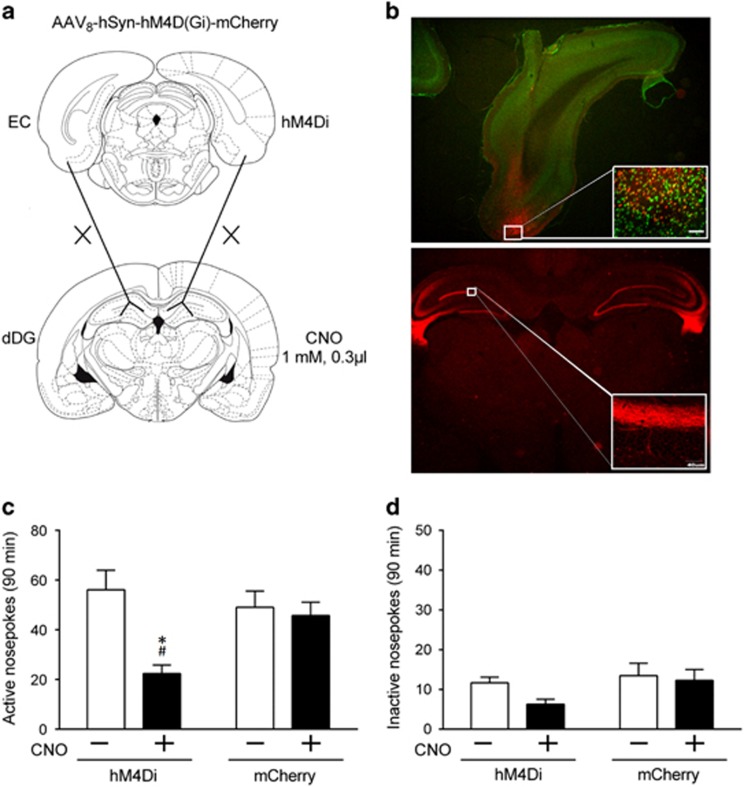
Figure 3.
Inhibition of EC–dDG projections decreased context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. (a) Projections from the EC to the dDG were transiently inactivated by microinjection of CNO in the dDG where the EC axon terminals expressing hM4Di receptors projected. (b) Representative DREADD expression in the experimental groups at 6 weeks after AAV8-hSyn-hM4D (Gi)-mCherry microinjected in the EC. Top, typical photomicrographs (× 1.25) for mCherry-tagged hM4Di (red) and NeuN (green) in the EC. Bottom, Example (× 1.25) of axonal labeling for the mCherry-tagged hM4Di receptor (red) in the dDG. (c) Number of active nose-pokes during context-induced reinstatement after intra-dDG vehicle or CNO treatment in animals with hM4Di virus expression or control. Two-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs CNO+ of control animals; *P<0.05, vs CNO- of hM4Di å n=11 per group. (d) No difference was observed in inactive nose-pokes during context-induced reinstatement after intra-dDG vehicle or CNO treatment in animals with hM4Di virus expression or control, two-way ANOVA; n=11 per group. Data are depicted as mean±SEM.