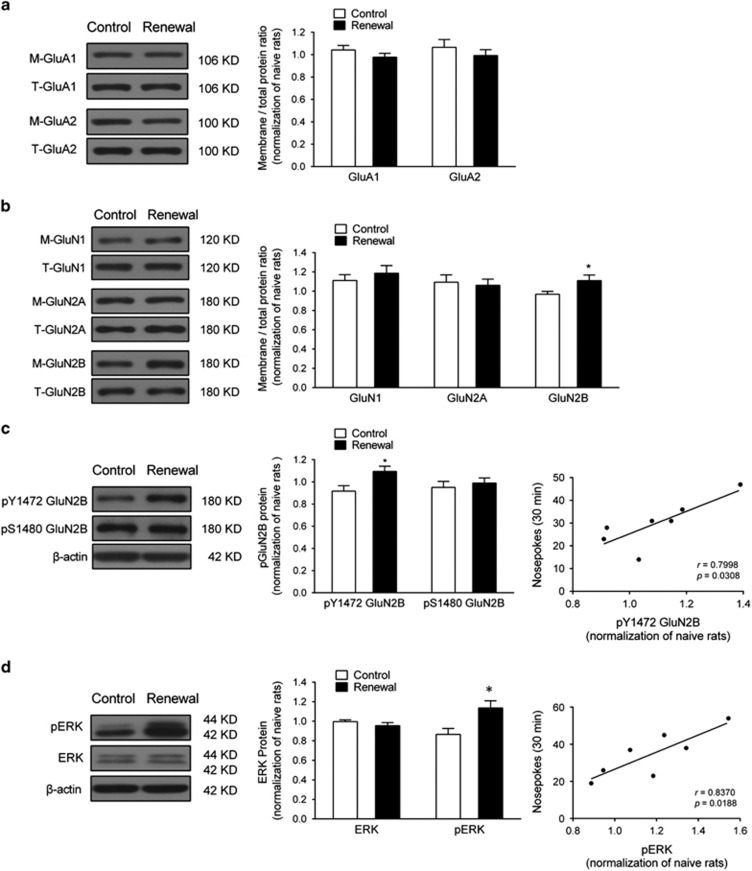
Figure 4.
Heroin-paired context reexposure elevated GluN2B–ERK1/2 signaling in the dDG. (a) Western blot analysis of AMPAR subunit GluA1 and GluA2 membrane/total protein level in the dDG after 30 min context-induced reinstatement testing. No difference was found between control and renewal group for GluA1 and GluA2 subunits using unpaired t-test, respectively; n=7 per group. (b) NMDAR subunit GluN1, GluN2A, and GluN2B membrane/total protein level in the dDG after 30 min context-induced reinstatement testing. *P<0.05 vs control group using unpaired t-test; n=7 per group. (c) GluN2B activation in the dDG after context-induced reinstatement testing. Left, western blot analysis of phosphorylation of GluN2B at Y1472 and S1480 in the dDG immediately after 30 min context-induced reinstatement testing. *P<0.05 vs control group using unpaired t-test. Right, correlation of context-induced reinstatement behavior with pY1472 GluN2B activation in the renewal group; n=7 per group. (d) ERK1/2 and pERK1/2 protein level in the dDG after 30 min context-induced reinstatement testing. Left, western blot analysis of phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and pERK1/2 in the dDG immediately after context-induced reinstatement testing. *P<0.05 vs control group using unpaired t-test. Right, correlation of context-induced reinstatement behavior with PERK1/2 activation in the renewal group; n=7 per group. Data are depicted as mean±SEM.