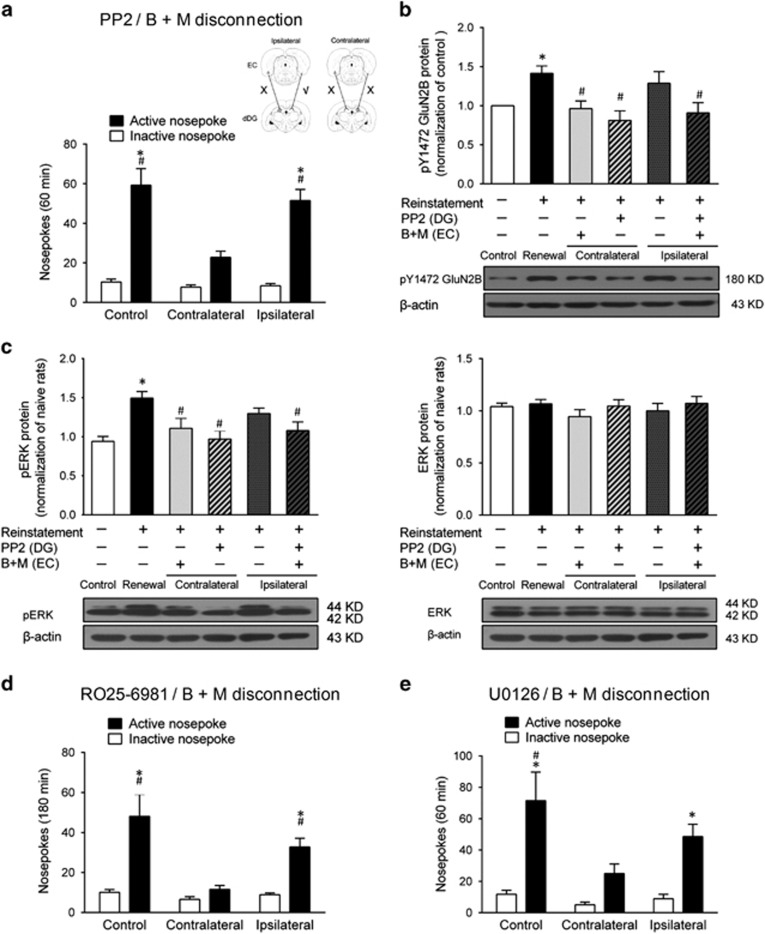
Figure 5.
Inhibition of EC–dDG projections via GluN2B–ERK1/2 signaling decreased context-induced reinstatement of heroin seeking. (a) Number of nose-pokes during context-induced reinstatement under PP2 and B+M disconnection treatment. Two-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs active nose-poke of contralateral disconnection animals; *P<0.05, vs inactive nose-poke of each group, n=10 per group. Insert, overview of the paradigm used in this experiment. (b) pY1472 GluN2B level in the dDG after 30 min context-induced reinstatement under the PP2 and B+M disconnection treatment. *P<0.05 vs control group using unpaired t-test. One-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs renewal group, n=7 per group. (c) pERK1/2 and ERK1/2 protein level in the dDG after 30 min context-induced reinstatement under the U0126 and B+M disconnection treatment. *P<0.05 vs control group using unpaired t-test. One-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs renewal group, n=5–7 per group. (d) Number of nose-pokes during context-induced reinstatement under RO25-6981 and B+M disconnection treatment. Two-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs active nose-poke of contralateral disconnection animals; *P< 0.05, vs inactive nose-poke of each group, n=9 per group. (e) Number of nose-pokes during context-induced reinstatement under U0126 and B+M disconnection treatment. Two-way ANOVA, #P<0.05 vs active nose-poke of contralateral disconnection group; *P<0.05 vs inactive nose-poke of each group, n=7 per group. Data are depicted as mean±SEM.