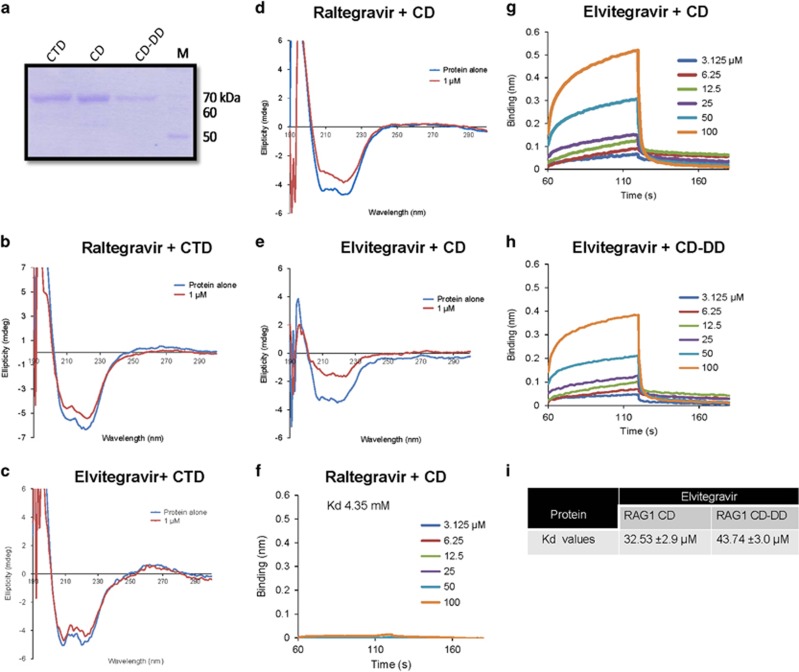
Figure 5.
Circular dichroism spectroscopy and biolayer interferometry to evaluate structural changes in different domains of RAG1 upon binding to integrase inhibitors. (a) SDS-PAGE showing the purified domains of RAG1 namely, C-terminal domain (CTD), central domain (CD) and central domain with the active site amino acids mutated (CD-DD). ‘M’ is molecular weight ladder. (b–e) The domains of RAG1 were incubated in presence 1 μM integrase inhibitors at 4 °C for 10 min and the spectra was taken using JASCO J-810 spectropolarimeter with a scan range of 200–260 nm. Circular dichroism spectra of C-terminal domain of RAG1 following incubation with 1 μM Raltegravir (b) and Elvitegravir (c). Spectra of central domain of RAG1 following incubation with 1 μM Raltegravir (d) and Elvitegravir (e). In all the cases, the spectrum of buffer with equivalent concentration of inhibitor was subtracted from that of protein with inhibitor. (f–h) Biolayer interferometry studies showing differential binding of Elvitegravir and Raltegravir to CD and mutant CD-DD. Biolayer interferometry sensorgrams depicting the real time binding of different concentrations of Elvitegravir and Raltegravir (0, 3.125, 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50 and 100 μM) to biotin-tagged purified proteins (1.4 nmol), CD (~70 kDa) (f and g) and mutant CD-DD (~70 kDa) (h) immobilised to SSA sensors. The sensorgrams curves depict the association, followed by dissociation of increasing concentration of inhibitors to the sensors. The real time binding curves were used to compute equilibrium dissociation constant (Kd) by globally fitting the rate equation for 1:1 kinetics to the data. The dissociation constant (Kd) value of Elvitegravir and Raltegravir for central domain of RAG1 is 32.53±2.9 μM and 4.35 mM, respectively. The dissociation constant (Kd) value of Elvitegravir for mutant CD-DD RAG1 is 43.74±3.0 μM. (i) Table shows Kd values obtained based on multiple batches of BLI for RAG1 CD and CD-DD with Elvitegravir