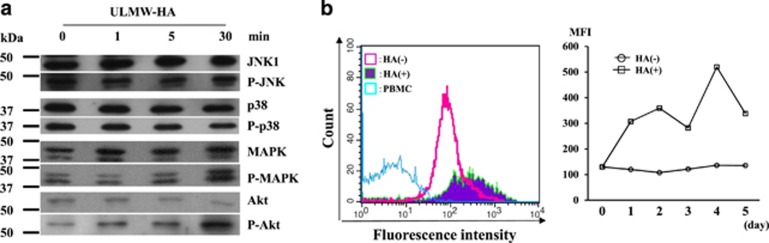
Figure 6.
Analysis of molecular mechanisms of cell death after ULMW-HA stimulation. (a) Western blot analysis of changes in activation status of signal transduction molecules. KOPB26 cells (5 × 106 per tube) were stimulated with ULMW-HA (10 mg/ml), and harvested at 1, 5 and 30 min. Cell lysates were separated, blotted and stained with antibodies against whole or phosphorylated form of JNK1, p38, MAPK and Akt. The bands were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence kit. (b) Flow cytometric analysis of changes in ROS production. CM-H2DCFDA, an intracellular ROS detector, was absorbed into KOPB26 cells, and then they (0.5 × 105 per well) were cultured in the presence or absence of ULMW-HA (2.5 mg/ml) for up to 5 days. The levels of intracellular ROS were analyzed before and at days 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 after ULMW-HA stimulation by flow cytometry. Left panel: flow cytograms of ROS production at day 3. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were used as a control. The left- and right-sided open cytograms show results of PBMC and after culture without HA, respectively, whereas the filled cytogram shows the result after culture with HA. Right panel: changes in ROS production. The data (MFIs) are representative from two separate experiments