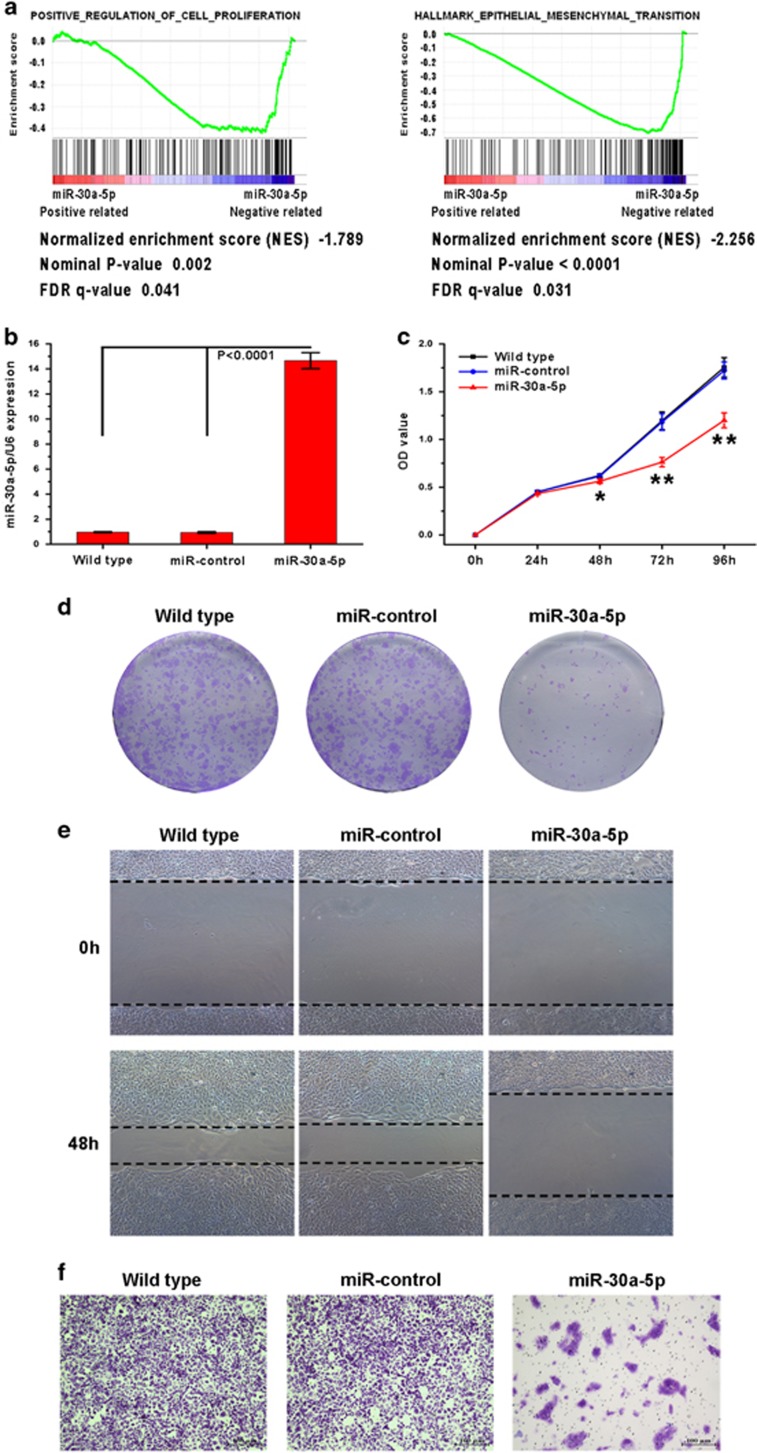
Figure 3.
Exogenetic expression of miR-30a-5p suppresses ccRCC cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion in vitro. (a) GSEA plots presenting the inverse correlation between miR-30a-5p expression with positive regulation of cell proliferation genes (left panel) and hallmark EMT genes (right panel) in the TCGA KIRC data set. (b) Real-time PCR analysis of miR-30a-5p in 769-P cells after exogenetic expression. (c) Cell growth of indicated cell as measured by CCK8 assay (*P<0.05 and **P<0.01 comparing exogenetic expression of miR-30a-5p and other treatments). (d) Effect of miR-30a-5p expression on ccRCC cell line colony formation. Representative colony formation results for wild-type, miR-control lentivirus-infected and miR-30a-5p lentivirus-infected 769-P cells, where the results were independently reproducible in triplicate. (e) Wound healing assay assessing cell motility in wild-type 769-P, miR-control 769-P and miR-30a-5p 769-P cells. Overexpression of miR-30a-5p notably inhibited the migration of 769-P cells. (f) Cell invasion was evaluated using the Matrigel invasion chamber, and miR-30a-5p overexpression clearly inhibited 769-P cell invasion