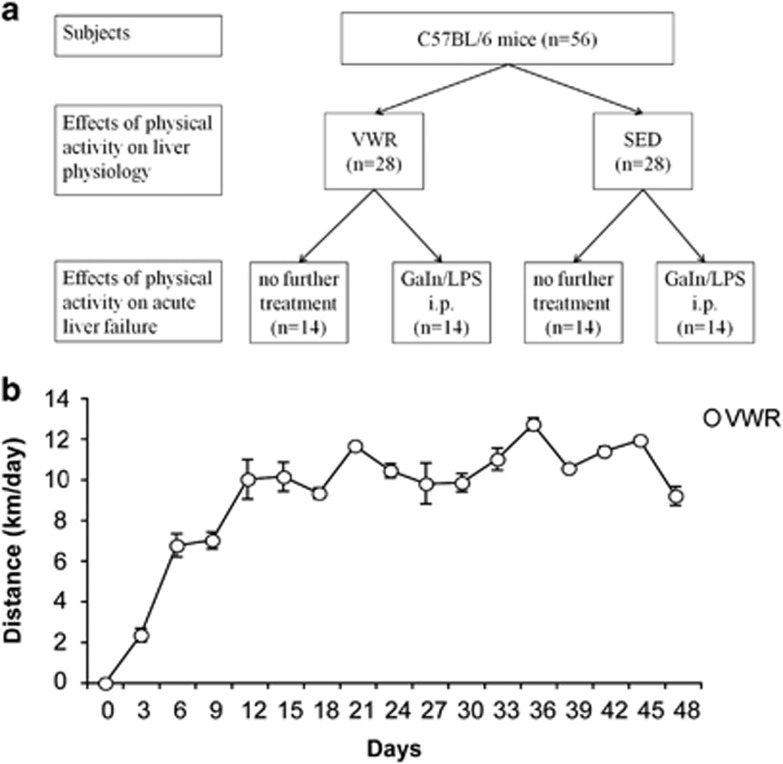
Figure 1.
(a) Experimental setup. Male C57BL/6 mice (n=56), aged 7–11 weeks, were randomly assigned to a voluntary wheel running (VWR, n=28) group or sedentary (SED, n=28) group. After a mean of 45 days 14 mice of each group were killed to examine the effects of voluntary physical activity. The remaining 14 mice of each group were injected intraperitoneally (i.p.) with LPS and GaIN to examine the effects of physical activity on acute liver failure. (b) Running distance. VWR distance was monitored continuously using a bicycle tachometer in single housed mice. Median distance is displayed over time from n=28 VWR mice