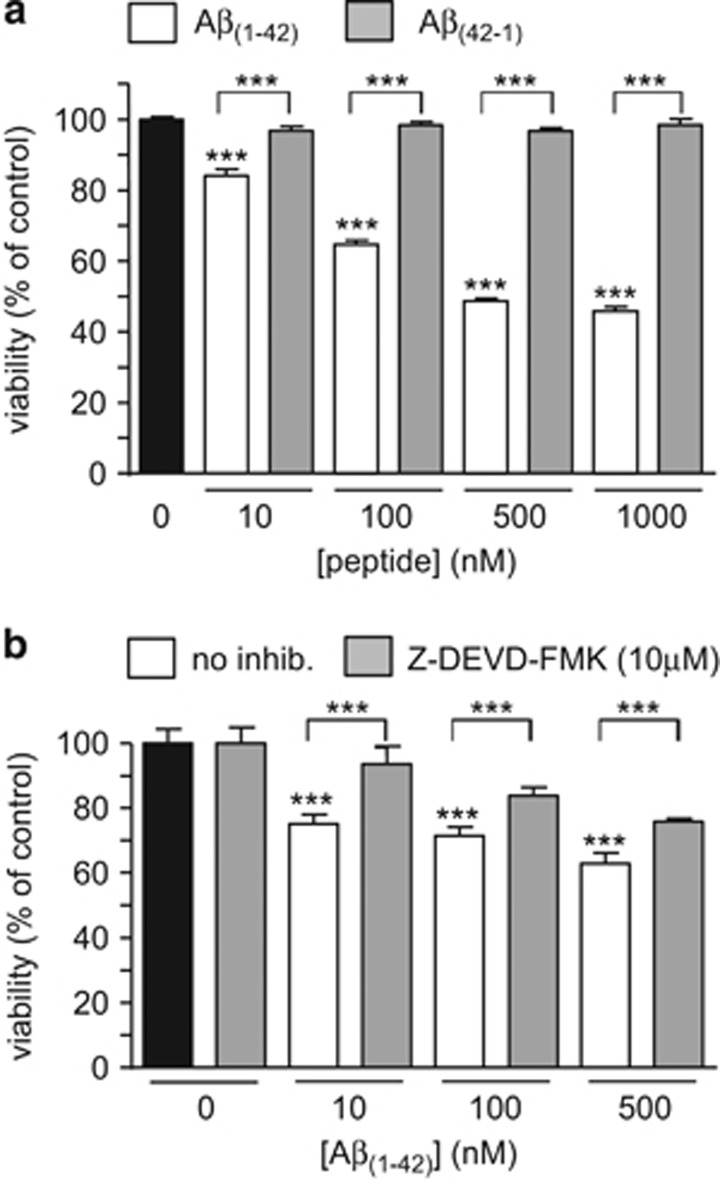
Figure 1.
Amyloid peptide Aβ1–42 is toxic to astrocytes in part via inducing apoptosis. (a) Effect on cell viability of a 24 h exposure of astrocytes to Aβ1–42 (10–1000 nM, white bars) and the reverse peptide Aβ42-1 (grey bars) using the mitochondrial activity-based MTT assay. Bars represent the mean±S.E.M. data of cells from 4 repeats (each performed in duplicate) with cells from different preparations. (b) as (a), except cells were exposed either to Aβ1–42 alone (10–500 nM, white bars) or Aβ1–42 in the additional presence of 10 μM Z-DEVD-FMK, a caspase-3 inhibitor (grey bars). Bars represent the mean±S.E.M. data of cells from 3 repeats (each performed in duplicate) with cells from different preparations. Significant difference: ***P<0.001 effects of peptide alone compared to control, or between amyloid peptide and reverse peptide (a), or effects of Z-DEVD-FMK at each amyloid concentration, as indicated