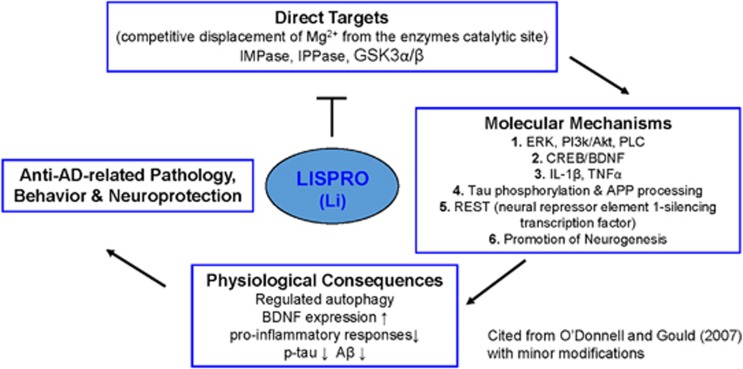
Figure 1.
Schematic illustration of the lithium targeted cellular and molecular mechanism by activating several neurotrophic and associated signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Lithium inhibit GSK3 (both α and β isoforms) and inositol mono/polyphosphatase (IMPase, IPPase) activity. The inhibition of GSK3 by lithium reduces tau phosphorylation and production of Aβ peptides by interfering γ-secretase cleavage of APP processing. In addition, inhibition of inositol monophosphatse by lithium may regulate clearance of aggregated phosphorylated tau and Aβ peptides. Moreover, lithium increases the expression of BDNF, which activates the ERK/MAPK pathway and further increases the expression of nuclear transcription factor cAMP response element (CREB). Accordingly, activation of BDNF may upregulates neurogenesis and downregulates pro-inflammatory responses (IL-1β and TNFα) in Alzheimer’s disease