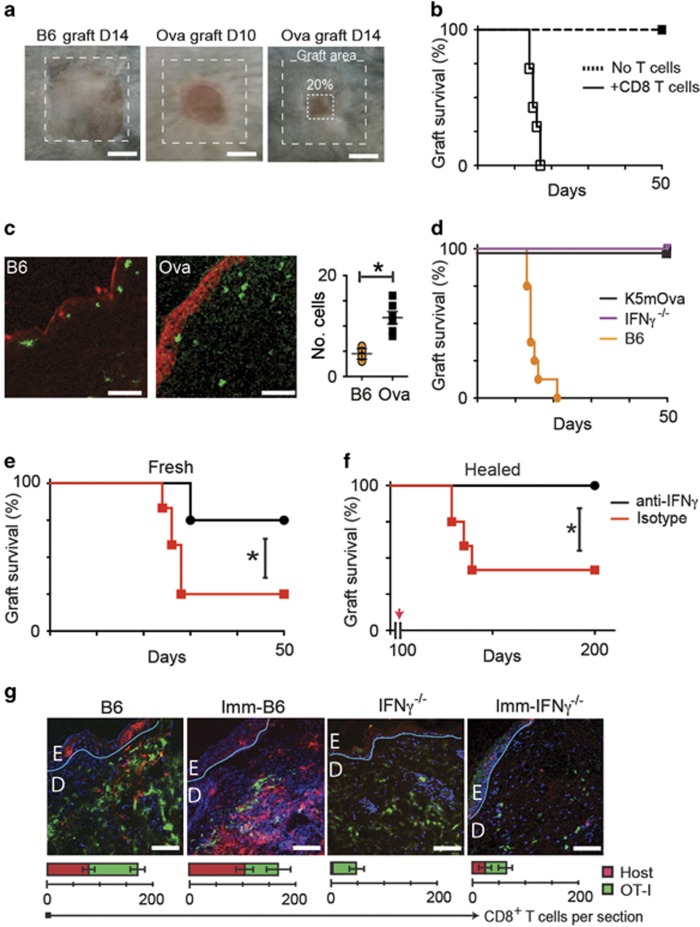
Figure 1.
Interferon-γ is required for skin graft rejection. Ear skin from B6 or K5mOVA donor mice was grafted on the flanks of B6 recipients. (a) 80% graft loss was denoted as rejection. (b) OVA skin grafted onto Rag1−/− mice with or without transferred 106 naive CD8 T cells. (c) Section of OVA grafts onto B6 or OVA mice at day 10 stained for caspase-3 (red), CD8 (green; Bar, 100 μm); quantified per field of view. Data pooled from 2 experiments, error bars are SEM. (d) OVA transgenic grafts were placed on K5mOva, IFNγ−/− or B6 recipients. Graph shows graft survival. (e) IFNγ−/− recipients received pre-primed CD8 cells by adoptive transfer, and were treated with anti-IFNγ or isotype antibody 48 h prior to grafting of OVA skin, and weekly thereafter. Graph shows graft survival (*P<0.05, Mantel–Cox test). (f) OVA skin grafts were placed on IFNγ−/− mice for 100 days. Recipients were then adoptively transferred with IFNγ-competent CTL, and anti-IFNγ or isotype antibody as in (e). (*P<0.001, Mantel–Cox test). (g) EGFP+ OT-1 CD8 T cells were adoptively transferred into OVA-naive B6 mice, OVA-immunized B6 mice, OVA-naive IFNγ−/− mice, or into OVA-immunized IFNγ−/− mice, before placing OVA skin grafts. Grafts were harvested after 10 days and stained for CD8. Confocal images were taken at graft edges and have been pseudocoloured to show native CD8 cells (red), transferred cells (green) and nuclei (blue). The basement membranes have been drawn in teal. (Bar, 100 μm). The average total cell numbers of T cells in each field from duplicate fields of two samples from a typical experiment is indicated in the graphs below. Error bars are S.D.