Fig. 2. Differential binding of R5 HIV-1 strains to control (unpolarized) and polarized monocyte-derived macrophage.
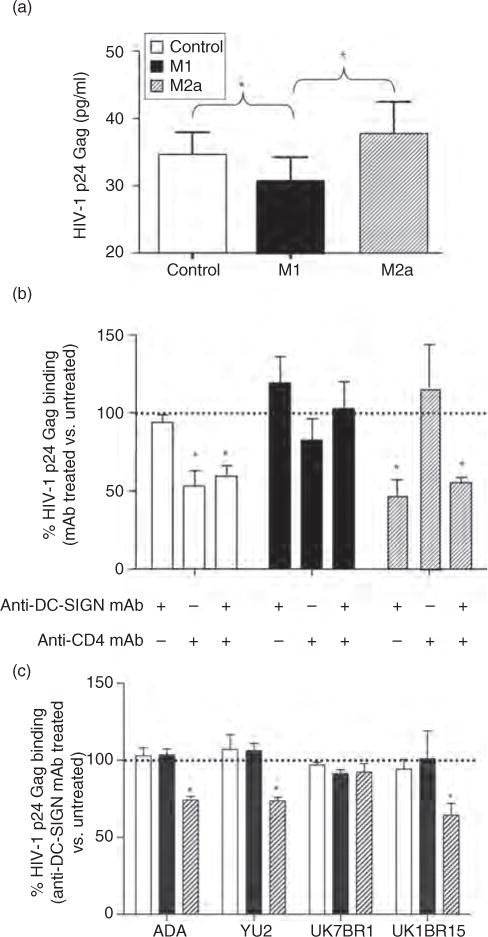
(a) HIV-1 binding to control (CD4highDC-SIGNlow), M1-MDM (CD4lowDC-SIGNneg) and M2a-MDM (CD4lowDC-SIGNhigh) was measured 18 h after polarizing or control conditions as the amount of HIV-1 p24 Gag antigen bound to the cell surface after removal of excess viral inoculums and extensive washing. The results are presented as the average cell surface bound p24 Gag antigen detected in MDM cultures established from eight individual donors. Significantly higher levels of binding of HIV-1 were observed in control and M2a-MDM vs. M1 cells. Differences were assessed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey post-tests. *P ≤ 0.05. (b) Anti-DC-SIGN mAb reduce HIV-1BaL binding to M2a, but not to control or M1-MDM, independently of CD4. Values represent the percentage positivity for p24 Gag antigen vs. control and polarized populations that were not incubated with the indicated mAb (dotted line). The results show the mean + SD of three replicates per each MDM culture established from eight independent donors. The statistical difference in p24 Gag binding between cultures incubated in the presence or absence of the indicated mAb was evaluated by a paired t-test. *P ≤ 0.05. (c) Anti-DC-SIGN mAb reduced binding of NL4-3 viruses expressing macrophage-tropic envelopes from HIV-1ADA, HIV-1YU2 and HIV-1UK1BR15, but not HIV-1UK7BR1, in M2a. As discussed above, values represent the percentage of bound p24 Gag on MDM preincubated with anti-DC-SIGN mAb compared with untreated cells. Shown is the mean + SD of experiments performed in triplicate from two independent donors. The statistical difference in p24 Gag binding between cultures incubated in the presence or absence of the indicated mAb was evaluated by a paired t-test. ANOVA, analysis of variance; DC-SIGN, dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion molecule-3 grabbing nonintegrin; MDM, monocyte-derived macrophage. *P ≤ 0.05.
