Fig. 5.
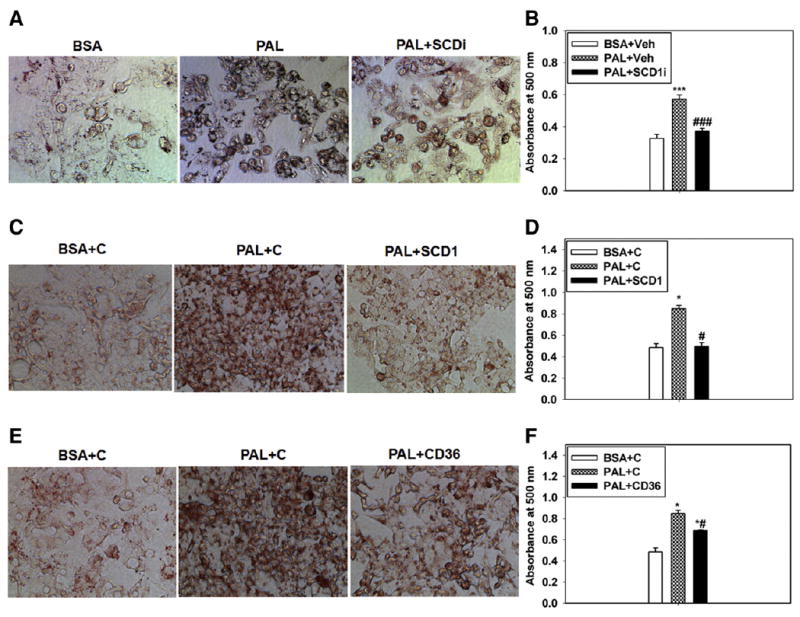
Inhibition of SCD1/CD36 prevents PAL-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells. Representative images of the ORO staining and the quantification of lipid accumulation by absorbance readings (which is normalized to total cell protein per well of the culture dish) in cells treated with BSA or PAL plus the vehicle or SCD1 inhibitor (A and B), BSA or PAL plus the negative control siRNA or SCD1 siRNA (C and D), and BSA or PAL plus the negative control siRNA or CD36 siRNA (E and F). Veh, dimethyl sulphoxide; SCD1i, SCD1 inhibitor; C, negative control siRNA. n = 3. *P < .05 and ***P < .001 vs BSA, respectively. #P < .05, ###P < .001 vs PAL, respectively. The results are presented as the means ± SEM.
