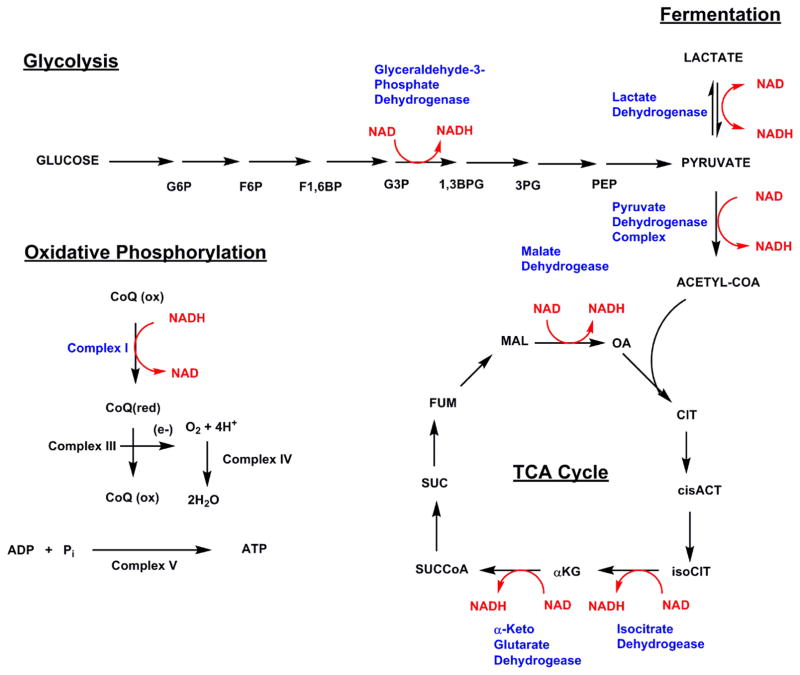
Figure 1. Integration of NAD+ and NADH into cellular energy metabolism.
NAD+ reduction to NADH is featured in glycolysis, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle). NADH oxidation to NAD+ occurs in the cytoplasm by action of lactate dehydrogenase and in mitochondria by action of Complex I. These oxidations maintain the high NAD+/NADH ratio maintained by mammalian cells and the majority of mitochondrial production of ATP is directly linked to Complex I activity. Abbreviations: glucose 6-phosphate, G6P; fructose-6-phosphate, F6P; fructose-1,6-bisphosphate, F1,6BP; glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 3-phosphoglycerate, 3PG; phosphoenol pyruvate; oxaloacetate, OA; citrate, CIT; cis-aconitate, cisACT; isocitrate, isoCIT; alpha-ketoglutarate, αKG; succinylCoA, SUCCoA; succinate, SUC; fumarate, FUM; malonate, MAL. Coenzyme Q, CoQ.