Fig. 8.
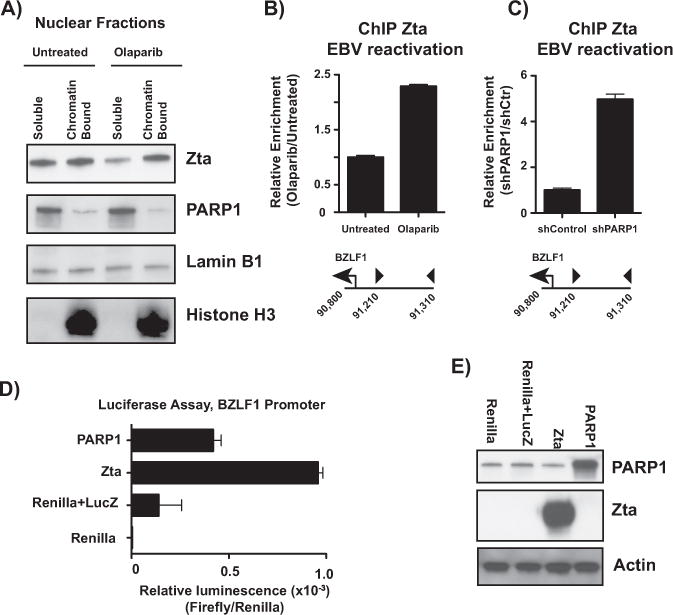
PARP inhibition and PARP1 knockdown increase Zta binding to the BZLF1 promoter. (A) Nuclear soluble and chromatin-bound fractions were extracted from Akata-EBV cells treated with and without olaparib. Fractions were subjected to western blot for Zta, PARP1, Lamin B1 as a nuclear control, and histone H3 as a chromatin fraction control. (B) ChIP-qPCR for Zta in Akata-EBV cells treated with and without olaparib at the BZLF1 promoter. Data are shown as relative enrichment over the untreated control. Data are representative of three independent experiments, and show mean ± standard deviation. (C) ChIP-qPCR for Zta in Akata-EBV cells infected with lentivirus carrying shRNA for PARP1 at the BZLF1 promoter. Data are shown as relative enrichment over the non-targeting control. Data are representative of three independent experiments, and show mean ± standard deviation. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with constructs expressing Renilla luciferase, firefly luciferase under control of the BZLF1 promoter (LucZ), plus constructs expressing Zta and PARP1. Data are shown as relative luminescence over Renilla luciferase, and show mean ± standard deviation. (E) Western blot of HEK293 lysates from transfection in (D). Blot was probed for PARP1 and Zta to confirm overexpression; actin served as a loading control.
