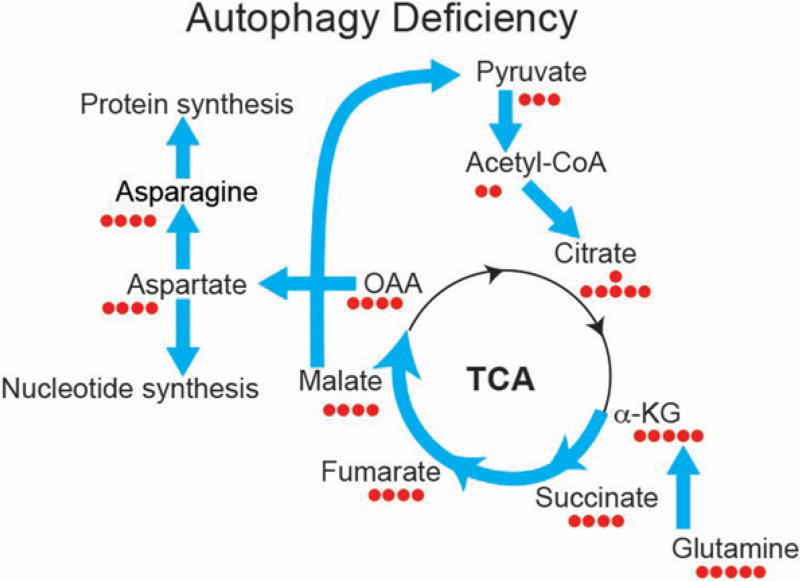
Figure 2.
Defective autophagy in tumor cells alters metabolic flux from glutamine to aspartate and to de novo nucleotide synthesis. K-ras-driven tumor cells depend on autophagy to supply the substrate glutamine and its derivatives to sustain mitochondria metabolism for starvation survival. To compensate, Atg7-deficient tumor cells significantly increase glutamine flux to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, de novo nucleotide synthesis, and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) generation by up-regulating flux from malate, pyruvate, acetyl-CoA, and citrate for antioxidant defense (Guo et al. 2016). OAA, oxaloacetate; α-KG, α-ketogluturate.