Figure 3.
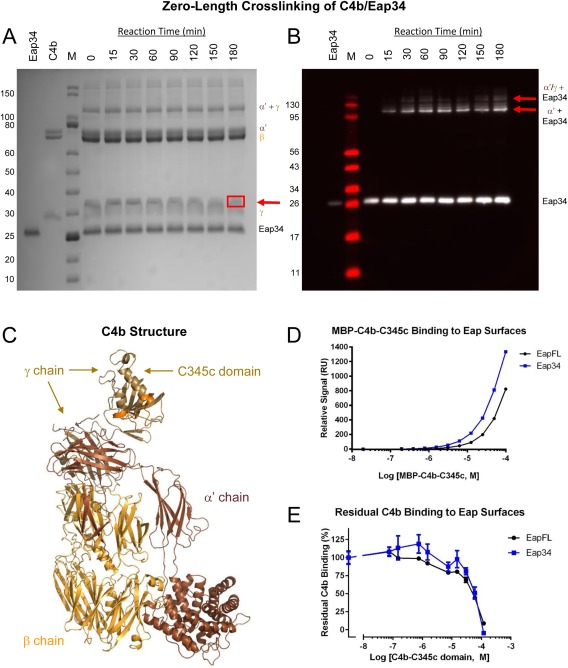
The Eap34 binding site involves both the α′‐ and γ‐chains of C4b. (A) Time‐dependent, zero‐length crosslinking between free amines of Eap34 and activated carboxylates of C4b. C4b was activated by treatment with EDC and NHS prior to incubation with Eap34. Aliquots were withdrawn over the course of 180 min, and the contents were denatured, reduced, and separated by SDS‐PAGE. While no time‐dependent changes were visible for either the α′ or β‐chains of C4b, loss of staining intensity of the γ‐chain correlated with the appearance of a band with altered mobility from that of the γ‐chain or Eap34 (red arrow). This band contained both Eap34 and γ‐chain, as judged by peptide fingerprinting analysis [Fig. S1(B), Supporting Information]. (B) An identical reaction series to that shown in panel A was prepared, separated by SDS‐PAGE under reducing conditions, and transferred to membranes for analysis by immunoblotting. A polyclonal anti‐Eap antisera raised in sheep readily detected recombinant Eap34, and additional adduct bands of higher apparent molecular weight corresponding to the α′‐chain + Eap34 and the α′/γ‐chains + Eap34 (red arrows). (C) A representation of the C4b structure (PDB Accession Code 4XAM23) is provided for clarity in interpreting SDS‐PAGE and blotting images. Each distinct polypeptide is colored differently, with the α′‐chain in brown, β‐chain in yellow‐orange, and γ‐chain in beige. The MIDAS‐acceptor site of the C345c domain, which mediates metal‐dependent binding of the vWF domain of C2 to C4b, is shaded orange. (D) Analysis of the dose‐response sensorgram data shown in Figure S2, Supporting Information, using a steady‐state binding model. (E) Competition binding between recombinant C4b‐C345c and native C4b, using the same biosensor surfaces shown in panel D. A fixed concentration of C4b was incubated with increasing concentrations of C4b‐C345c, and the residual binding of C4b was determined following co‐injection in triplicate. Notably, the midpoint of both curves in this study correspond well to the affinities observed in the MBP‐C4b‐C345c direct binding studies of panel D and Figure S2, Supporting Information.
