Figure 5.
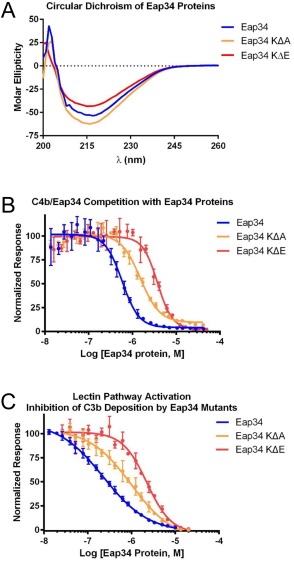
Eap34 lysine residues identified by chemical footprinting contribute to C4b binding. The contribution of Eap34 lysines to C4b binding was explored by site‐directed mutagenesis, wherein the seven protected lysines were mutated in concert to either alanine (Eap34‐KΔA) or glutamate (Eap34‐KΔE). (A) CD Spectropolarimetry was used to assess the secondary structure content of Eap34, as well as the Eap34‐KΔA and Eap34‐KΔE mutants. (B) The ability of untagged Eap34 and both mutants to compete the AlphaScreen signal generated by myc‐Eap34 and C4b‐biotin was assessed over a logarithmic dilution series. All assay points were conducted in triplicate prior to fitting to a dose‐response curve. (C) Lectin pathway activity in the presence of Eap34 and both mutants was assessed by ELISA specific for C3b. All assay points were conducted in triplicate prior to fitting to a dose‐response curve. Legends are inset.
