Figure 2.
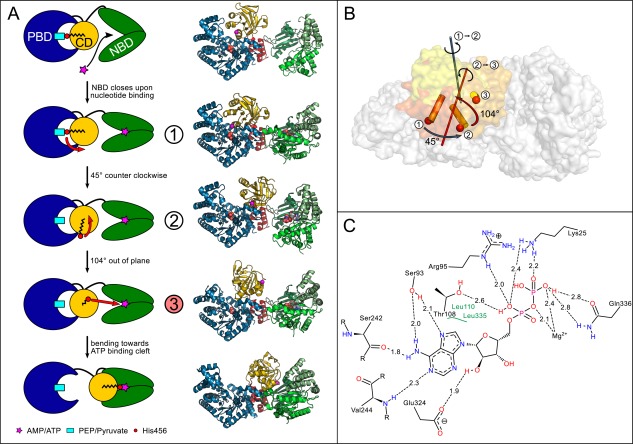
(A) Schematic model of the CD movement in the catalytic cycle taking into account currently known conformational intermediates. Helix 20 containing the catalytic His456 (red circle) at its N‐terminal end is drawn as black zig‐zag structure. The different CD conformations are numbered according to (B) with the newly solved intermediate structure highlighted in red. Corresponding crystal structures are shown on the right from top to bottom: 5JVJ chain A, 5JVL chain D, 5JVN, 5LU4 chain A 6, 1KBL 7. (B) Illustration of PPDK‐CD structural intermediates. CDs of published structures 5JVL chain C (1, dark‐orange), 5JVN (2, orange), and of newly resolved structure 5LU4 (3, yellow) as well as the corresponding rotational axes for transformation between the different intermediate states are shown. (C) Schematic representation of the nucleotide binding site in 5LU4 chain A containing tightly bound ADP. The distances between the bound nucleotide and interacting amino acids of the binding pocket are given in Å. An interactive view is available in the electronic version of the article
