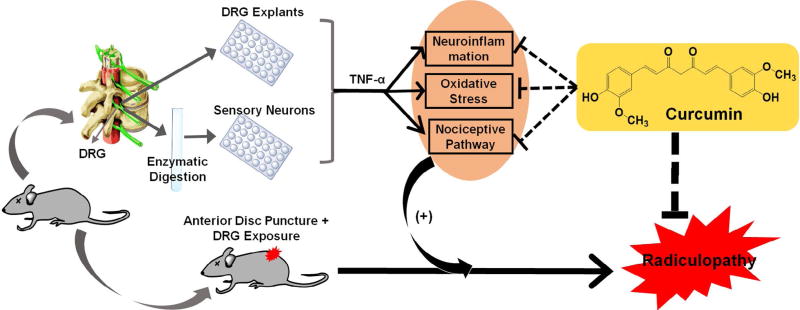
Fig. 7.
Schematic hypothesis of the current study in exploring curcumin’s therapeutic potential to combat radiculopathy secondary to disc herniation: 1) In vitro pleiotropic functions of curcumin via via attenuating attenuation of TNF-α -induced neuroinflammation, ROS production and nociceptive factors in isolated mouse DRG and primary neurons; 2) In vivo analgesic effect of systemically administered curcumin in a mouse model of lumbar radiculopathy secondary to disc herniation.