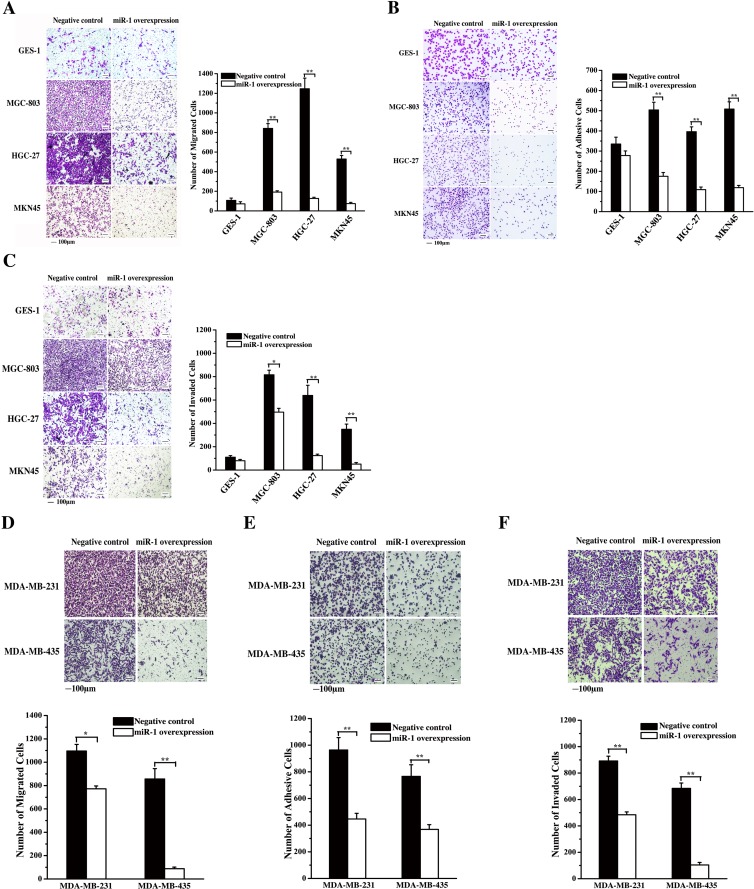
Figure 4. Effects of miR-1 on gastric and breast cancerous cell metastasis.
A. Effect of miR-1 on gastric cancer cell metastasis. Gastric cancer cells (MGC-803, HGC-27 and MKN45) and the normal cells (GES-1) were transfected with the miR-1 precursor or the negative control. At 48 h after transfection, cell migration was examined, and the data were analyzed. Representative images are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm. B. Effects of miR-1 overexpression on the adhesion of gastric cancer cells. The cells were transfected with the miR-1 precursor or the negative control and then cultured for 48 h. The number of adherent cells was evaluated. Representative images are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm. C. The role of miR-1 in cancer cell invasion. miR-1 precursor-transfected cells were cultured for 48 h. Then, the cells were characterized with cell invasion assays. Scale bar, 100 μm. D. Evaluations of breast cancer cell migration. MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 cells were transfected with 30 nM of the miR-1 precursor or the negative control miRNA to overexpress miR-1. At 48 h after transfection, the migrated cells were examined. Representative images are shown. Scale bar, 100 μm. E. The influence of miR-1 overexpression on breast cancer cell invasion. At 48 h after miR-1 overexpression, the invaded cells were evaluated. Representative images are provided. Scale bar, 100 μm. F. Cell adhesion assays. Breast cancer cells treated with the miR-1 precursor were cultured for 48 h, then, the adherent cells were examined. Representative images are indicated. Scale bar, 100 μm. In all panels, asterisks represent statistically significant differences between treatments (*, p < 0.1; **, p < 0.05).