Figure 6. Prohibitin accumulation protects against tunicamycin-induced cell death.
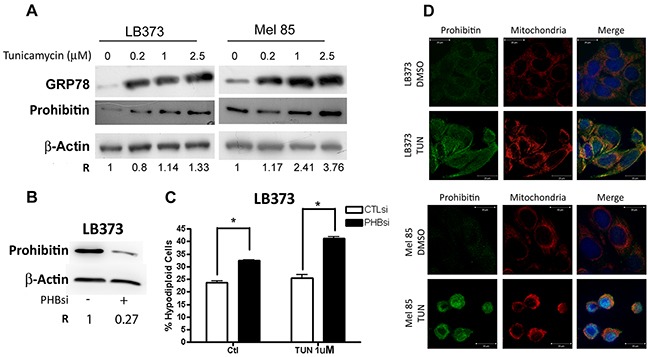
Cells were either treated 0.2 μM, 1.0 μM or 2.5 μM of tunicamycin, or left untreated (ctl) for 24 h. (A) Tunicamycin can induce PHB accumulation in a dose-dependent manner in LB373 and Mel 85 cell lines. Accumulation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress marker grp78 was used as a positive control for the tunicamycin treatment. (B) Prohibitin knock-down using PHBsi led to c.a. 70% reduction in the accumulation of PHB, as compared to control siRNA, as analyzed by western blots. (C) Upon PHB knock down, LB373 cells were more sensitive to tunicamycin induced cell death (1.0 μM tunicamycin), altogether the results indicate that PHB accumulation is also part of the unfolded protein response (UPR). (D) Analysis of PHB compartmentalization upon tunicamycin treatment was performed as in Figure 5. After tunicamycin treatment, PHB (green) was mainly colocalized with mitochondria (red) in LB373 and Mel 85 cell lines, although PHB could also be found in the nucleus to a certain extent. Scale bar in white (5μM). Representative experiment of two independent assays.
