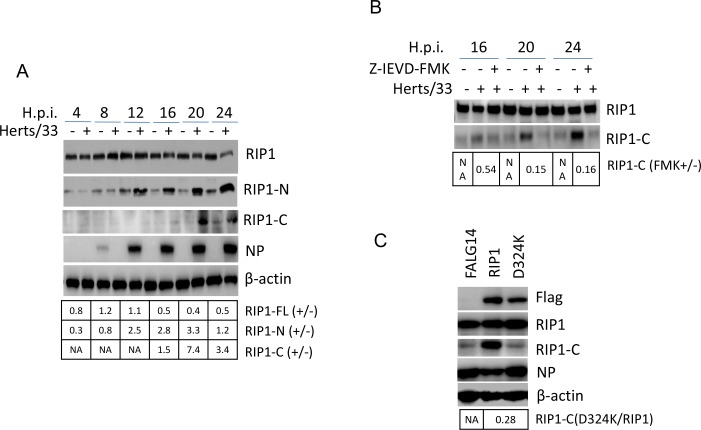
Figure 4. The cleavage of RIP1 at D324 by caspase 8 promotes apoptosis during NDV infection.
(A) RIP1 is cleaved during NDV infection. Cells samples in Figure 1A were analyzed with Western blot to check the cleavage of RIP1, using anti-RIP1-N or anti-RIP1-C. The intensities of bands were determined by densitometry, normalized to β-actin, and shown as fold change (virus : mock). (B) The cleavage of RIP1 is dependent on caspase 8 activity. HeLa cells were mock-infected or infected with NDV, followed by the treatment of DMSO or 40 μM Z-IEVD-FMK. Cells were harvested at 16, 20, and 24 h.p.i. and the cleavage of RIP1 was analyzed with Western blot using anti-RIP1-C. The intensities of RIP1 and RIP1-C bands were determined by densitometry, normalized to β-actin, and shown as fold change (FMK+/−). (C) RIP1 is cleaved at D324 during NDV infection. HeLa cells were transfected with Flag14, Flag14-RIP1, and Flag14-D324K for 20 h, followed by NDV infection. Cells were harvested at 20 h.p.i. and subjected to Western blot analysis to examine the expression and cleavage of RIP1. The intensities of RIP1-C bands were determined by densitometry, normalized to β-actin, and shown as fold change (D324K/RIP1).