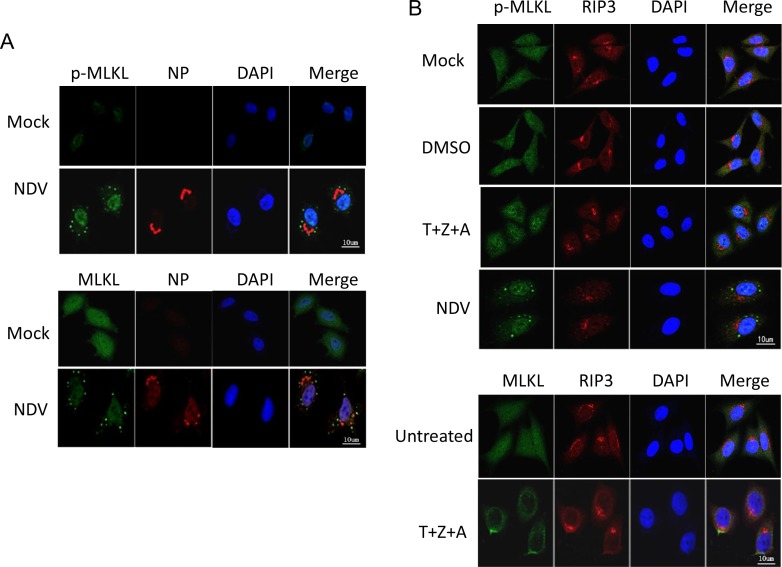
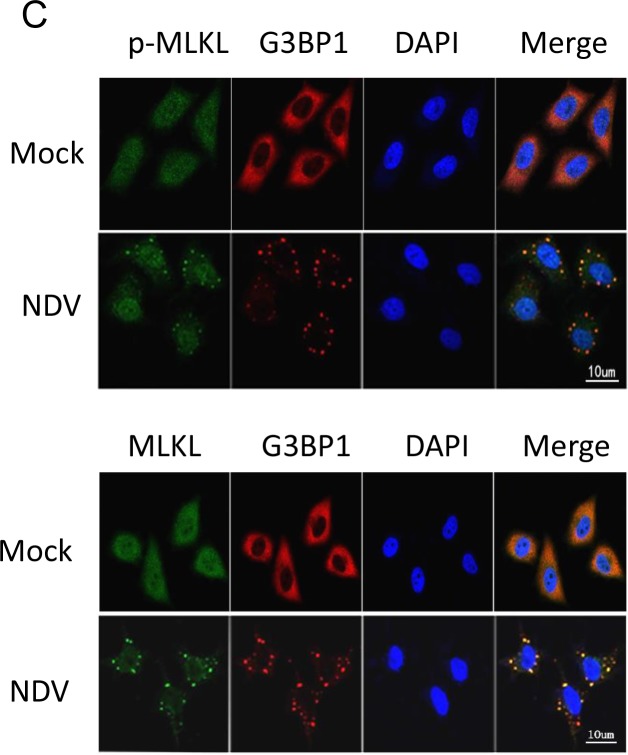
Figure 7. MLKL clusteres to SGs during NDV infection, instead of plasma membrane translocation.
(A) MLKL aggregates to punctate structure in the cytoplasm during NDV infection. HeLa cells were mock-infected or NDV-infected for 16 h. The subcellular distribution of phosphor-MLKL or total MLKL (green), and NP (red) were examined with immunostaining. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Merged images illustrate p-MLKL/NP/DAPI or MLKL/NP/DAPI fluorescence. (B) MLKL moves to plasma membrane by treatment of necroptosis stimulators (T+Z+A). HeLa cells were treated with necroptosis stimulators TNF-α, Z-VAD-FMK, and AT406 (T+Z+A) for 10 h. The subcellular distribution of phosphor-MLKL or MLKL (green), and RIP3 (red) were examined with immunostaining. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Merged images illustrate MLKL/RIP3/DAPI fluorescence. (C) MLKL is co-localized with SGs hallmark G3BP1 during NDV infection. HeLa cells were mock-infected or NDV-infected for 16 h. The subcellular distribution of phosphor-MLKL or MLKL (green), and G3BP1 (red) were examined with immunostaining. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Merged images illustrate MLKL/G3BP1/DAPI fluorescence.