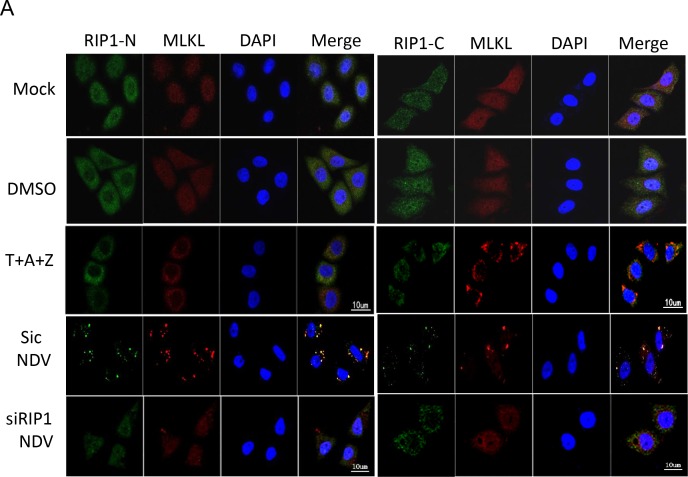
Figure 8. RIP1 binds to MLKL and recruits MLKL to SGs.
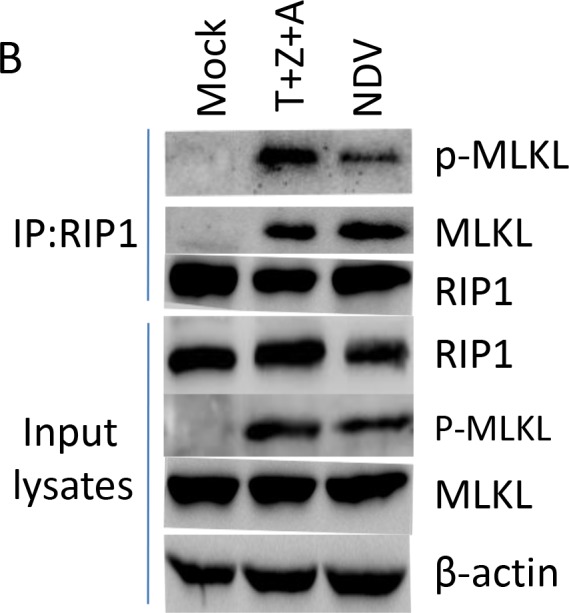
(A) Depletion of RIP1 prevents MLKL aggregate to SGs. HeLa cells were transfected with non-target siRNA or RIP1 siRNA for 36 h, followed with NDV infection for 16 h. Mock-infected cells, DMSO, T+A+Z stimulated cells were included as control. The subcellular distribution of RIP1 (green) and MLKL (red) was examined with immunostaining with anti-RIP1-N, or anti-RIP1-C, and anti-MLKL. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Merged images illustrate RIP1-N/MLKL/DAPI or RIP1-C/MLKL/DAPI fluorescence. (B) RIP1 binds to MLKL upon T+Z+A stimulation or NDV infection. HeLa cells were mock-infected, NDV-infected for 16 h, or stimulated with T+Z+A for 10 h, and subjected to immunoprecipitation using anti-RIP1-N. The pull down proteins and whole cell lysates were analyzed with Western blot.